Description
Toluene hydroalkylation is an important chemical process in the petrochemical industry, in which toluene (an aromatic hydrocarbon) reacts with hydrogen to produce benzene and methane. This process is very important for the production of high-purity benzene, which is a raw material for many chemical products.
Hydroalkylation Reaction
The hydroalkylation reaction of toluene can be represented as follows:
C₆H₅CH₃ + H₂ → C₆H₆ + CH₄
As can be seen in the above reaction, a methyl group (CH₃) is removed from the toluene molecule and forms a methane molecule along with a hydrogen atom. As a result, a benzene molecule is produced.
Reaction Conditions
To carry out the hydroalkylation reaction, certain conditions are required:
Temperature: The reaction is carried out at high temperatures (usually between 500 and 660 °C).
Pressure: The reaction is carried out at high pressures (usually between 20 and 60 bar).
Advantages of the Toluene Hydroalkylation Process
Production of high-purity benzene: This process is an efficient way to produce high-purity benzene.
Use of cheap raw materials: Toluene is a relatively cheap and readily available material.
Flexibility: The process can easily respond to changes in demand for benzene.
Applications of the Benzene Produced
Benzene produced through the hydroalkylation of toluene is used in the production of many chemical products, including:
Plastics: such as polystyrene and nylon، Paints and inks ،Detergents ،Adhesives ،Pharmaceuticals.
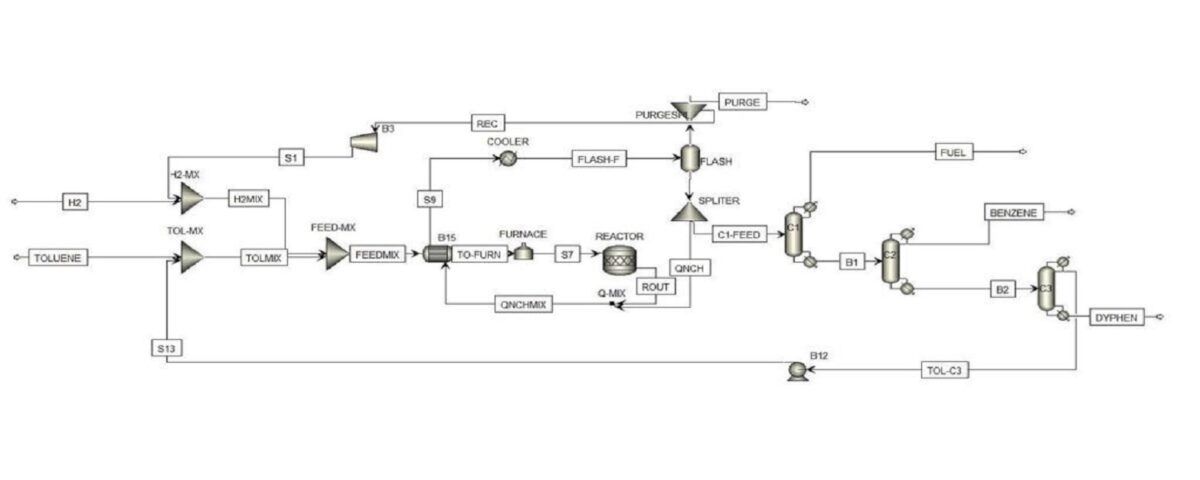
Toluene and hydrogen are converted in a catalyst-filled bed reactor to produce benzene and methane. Typically the reaction reaches 90% conversion and The reaction is highly exothermic and typical operating conditions are at temperatures of 500 to 660 °C and pressures of 20 to 60 bar. The figure below shows the PFD of the HDA process.
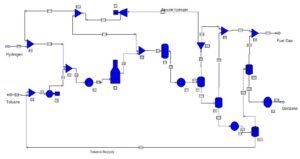
The simulation of this process has been done with Aspen Plus software. This project has an English report file.