Introduction
With the escalating global energy demand, fossil fuels continue to dominate the primary energy supply. However, given their finite reserves, the search for sustainable and alternative feedstock sources has intensified. Among the various feedstock options for ammonia production, R-LNG has emerged as a promising choice. Ammonia is synthesized from a 1:3 gaseous mixture of N2 and H2. This project aims to simulate a synthesis gas production unit using Aspen HYSYS, focusing on the activation of regasified liquefied natural gas (R-LNG) as the feedstock. The simulation is based on the conditions and parameters (mass flow rate, temperature, and pressure) obtained from the Fertilizer and Chemicals Travancore (FACT) ammonia plant.
Process Description
The overall ammonia production process can be divided into two main sections: (1) synthesis gas production (feedstock preparation) and (2) ammonia synthesis. Synthesis gas production involves unit operations such as desulfurization, steam reforming (primary reforming), air reforming (secondary reforming), CO shift conversion, CO2 removal, and methanation.
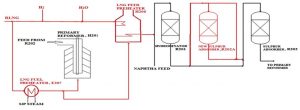
The desulfurization section consists of two stages: pre-desulfurization (PDS) and final desulfurization (FDS). In PDS, organic sulfur compounds are catalytically converted to hydrogen sulfide and then removed by distillation. This stage reduces the sulfur content in the feedstock from 1000 ppm to 10 ppm. In FDS, further catalytic hydrogenation of residual organic sulfur compounds is carried out, followed by the absorption of hydrogen sulfide on zinc oxide.
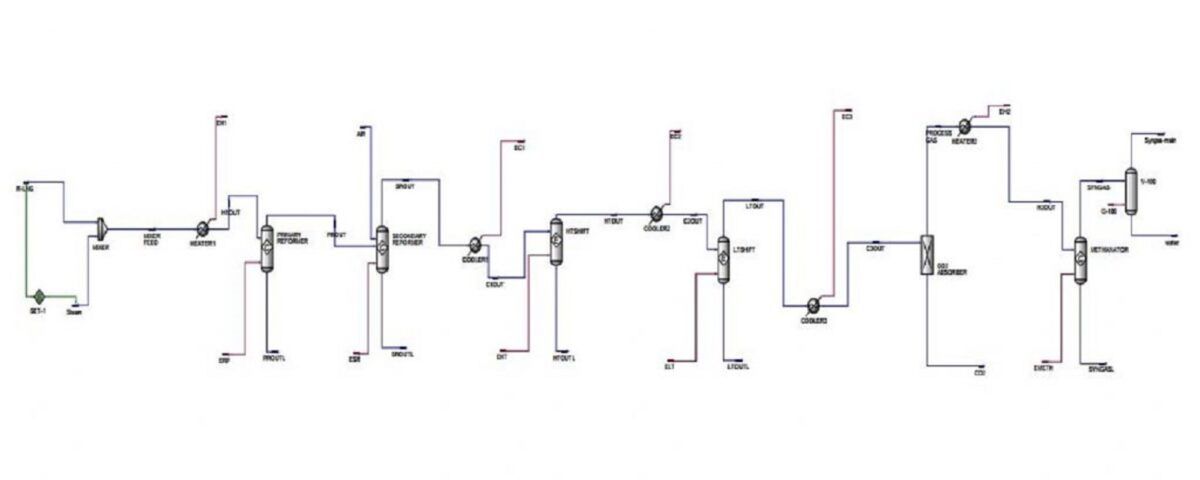
The ammonia synthesis section requires a feed stream of N2 and H2 in a stoichiometric ratio of 1:3, referred to as synthesis gas. To achieve this, the reforming reaction is divided into two stages: primary reforming and secondary reforming. In the primary reformer, hydrocarbon reforming occurs in the presence of steam. This reaction is controlled to maintain 10.5% hydrocarbon in the outlet stream, which is necessary for complete air reforming in the secondary reformer. The figure below shows the process flow diagram (PFD).
Secondary Reforming and Gas Synthesis
In the secondary reformer, nitrogen for ammonia synthesis is obtained through air reforming. The heat required for this process is supplied by combusting a portion of the gas-air mixture. The combustion of the gas provides the heat for the remaining reforming process and The effluent stream from the reforming section contains H₂, N₂, CO, CO₂, and 0.3 mol% unreacted hydrocarbons.
Since ammonia synthesis requires only nitrogen and hydrogen, the complete removal of carbon oxides from the raw synthesis gas is essential.
Aspen HYSYS Simulation and Economic Analysis of Syngas Production
This project simulates the syngas production process using Aspen HYSYS software, and the economic analysis is performed manually. A comprehensive report (in PDF format) is available.