Introduction
Heat transfer during boiling is highly efficient because the temperature of the substance remains constant. Since heat is transferred from the interface between liquid and vapor, surface tension plays a crucial role in studying this phenomenon. Researchers like Ludovici and colleagues have explored the effects of factors such as Marangoni convection, magnetic fields, and buoyancy due to temperature differences on heat transfer, where surface tension is a key factor. Additionally, Rimkevich and Zapalovich emphasized the importance of surface tension in the evaporation process of droplets in nucleate boiling.
To model various mechanisms governing fluid motion in porous media, it is essential to simulate surface tension and interfacial stress between the contacting phases. The cubic equation of state is used for surface tension modeling due to its suitable performance in predicting phase equilibrium calculations for systems involving polar compounds, compared to van der Waals-type equations.
Process Description
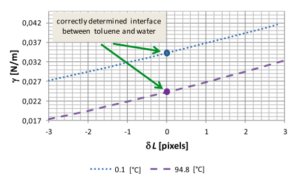
The method is based on measurements taken from digital images of droplets at the moment they form. Validation of this method was conducted against results from other researchers. The interfacial surface tension between water and toluene was determined in the temperature range of 0.1 to 96.6 °C, remaining approximately constant up to 40 °C before decreasing linearly until 80 °C, with a significant drop observed up to 96.6 °C. Uncertainty in the determined values was also estimated. Near the boiling point, the gas phase appears, making the surface tension indistinguishable. The experimental results are presented using a logistic function.
Conclusion
A novel method for determining surface tension was successfully applied to two immiscible liquids. The experimental setup is not highly advanced, and the calculations are straightforward. Surface tension between water and toluene remains relatively stable up to 40 °C before decreasing, while surface tension above 80 °C shows a significant reduction.
This project was conducted by ANILCO based on a research article.
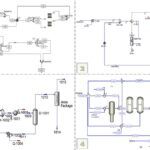
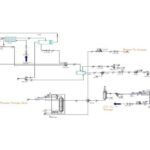
Surface Tension Simulation of Water-Toluene Mixture Using HYSYS
In this project, the surface tension of a water-toluene mixture was simulated using Aspen HYSYS version 14.