Introduction
Static simulation of the demethanizer using Aspen Plus software is recognized as a practical and essential tool in the design and optimization of processes in the petrochemical industry. Demethanizers play a key role in gas separation processes, particularly in the natural gas industry. These units are utilized to remove methane from hydrocarbon mixtures and to produce higher-purity products.
Aspen Plus, with its advanced capabilities for simulating and modeling chemical processes, provides the means for precise analysis of thermodynamic behavior and material flow. By using this software, it is possible to conduct accurate simulations and optimize the performance of demethanizers, thereby contributing to cost reduction and improved efficiency in petrochemical processes.

Demethanizer
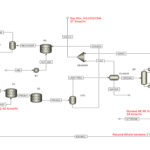
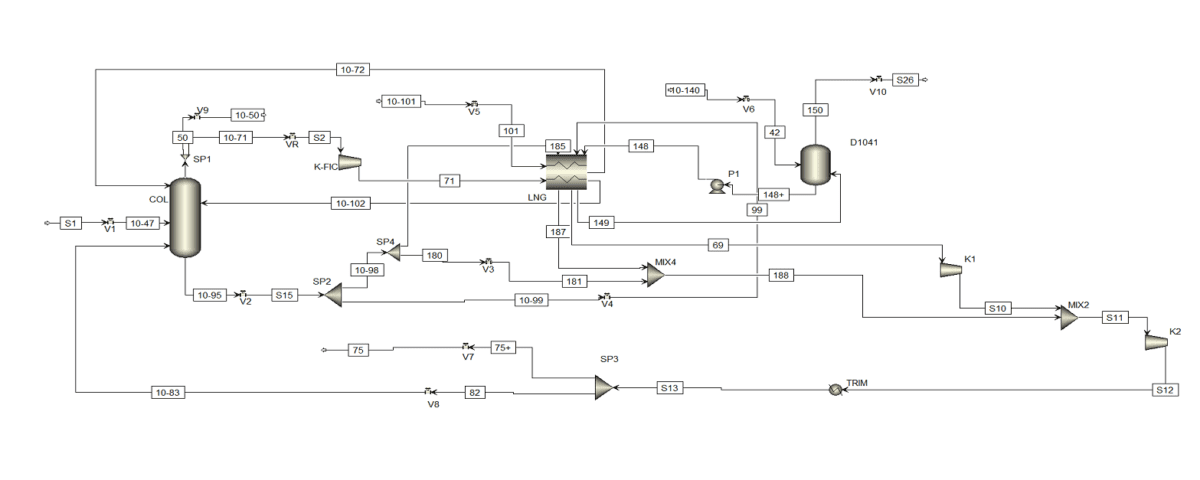
The demethanizer is one of the key pieces of equipment in the separation and purification processes of natural gas. It is specifically designed to remove methane from hydrocarbon mixtures, aiding in the production of high-purity products. Demethanizers are commonly used in the petrochemical and natural gas industries and serve as a means of separating heavier hydrocarbons from methane. The operation of the demethanizer is based on thermodynamic separation principles and typically occurs in two main stages: evaporation and distillation. In this process, the hydrocarbon mixture enters the demethanizer and is subjected to specific temperature and pressure conditions.
Feed Mixture:
The natural gas mixture is fed into the demethanizer. This mixture includes methane along with heavier hydrocarbons such as ethane, propane, and butane.
Distillation:
In this stage, temperature and pressure are adjusted using a heat exchanger. By decreasing the temperature and increasing the pressure, the heavier hydrocarbons are converted into liquid form and separated from methane.
Separation:
The produced liquid is transferred to a distillation column, where further separation occurs. In this column, heat and mass transfer are continuously carried out using trays or packing materials.
Product Output:
Ultimately, methane is discharged as the lighter product from the top of the column, while the heavier hydrocarbons are collected from the bottom of the column.
Design and Structure:
A demethanizer typically consists of the following components:
– Distillation Column: Includes trays or packing to optimize heat and mass transfer.
– Heat Exchanger: Used to control temperature and pressure, providing optimal conditions for separation.
– Pumps and Compressors: For the transfer and compression of gases and liquids.
– Control Systems: For monitoring and adjusting operational parameters.
Parameters Affecting Performance:
Various parameters influence the performance of a demethanizer, including:
– Temperature and Pressure: Precise adjustment of these two parameters aids in the effective separation of hydrocarbons.
– Feed Flow Rate: The quantity and composition of the incoming mixture significantly impact the performance of the demethanizer.
– Column Design: The type and design of trays and packing materials affect the efficiency of the distillation process.
Importance in Industry:
Demethanizers are highly significant in the petrochemical and natural gas industries due to their ability to produce high-purity products and reduce operational costs. They contribute to the optimization of separation processes and address the growing demands for energy and raw materials across various industries. Given the high demand for quality and high-purity hydrocarbons, optimizing the performance of demethanizers is one of the major challenges in the petrochemical industry.
Static Simulation:
Static simulation refers to the analysis and modeling of a chemical process under steady-state conditions. In the case of a demethanizer unit, static simulation involves examining and analyzing the performance of this unit when the system has reached equilibrium and the operating parameters remain unchanged.
Performance Analysis:
By utilizing static simulation, the performance of the column can be analyzed. This includes examining the rate of methane separation from other hydrocarbons, calculating the purity of the final products, and analyzing the effects of temperature and pressure variations on the column’s efficiency. This information helps engineers identify the strengths and weaknesses of the process.
Optimization:
Static simulation enables engineers to optimize operational conditions. For example, the feed ratio, temperature, and pressure can be adjusted to achieve the best performance and the lowest operational costs. This means maximizing separation efficiency while minimizing energy consumption.
Ultimately, the results of static simulation can serve as a basis for designing and optimizing real operational systems. These results allow engineering teams to make better decisions regarding the design and operation of the demethanizer unit.
Advantages of the Process:
Static simulation of this process allows engineers and designers to analyze and optimize the system’s performance. By utilizing simulation, operational parameters such as temperature, pressure, and the number of column stages can be varied to achieve the best efficiency and the lowest operational costs.
License:
Additionally, this process is conducted under the license and technology of Linde. This company is a global leader in gas separation and petrochemical technologies, leveraging its expertise and technologies across various projects.

Conclusion:
The static simulation of the demethanizer, as a key stage in the gas separation process, has provided valuable insights into the performance of this petrochemical unit. The use of Aspen Plus software, due to its advanced capabilities in modeling and analyzing chemical processes, has enabled engineers to accurately simulate processes and examine the system’s behavior under various conditions.
Furthermore, Linde’s license, as a credible source of thermodynamic data, has enhanced the accuracy and reliability of the simulation results, leading to greater confidence in the findings and analyses obtained. This data can assist in identifying strengths and weaknesses in the design and operation of the demethanizer, paving the way for process optimization. Ultimately, this simulation will not only contribute to improving efficiency and reducing costs at the Imam Khomeini petrochemical unit but can also serve as a foundation for future research and the development of new technologies in the petrochemical industry.
Sample Completed Project:
Static and Dynamic Simulation of 105, 106, 107 ASALOUYE with Aspen Plus
Static Simulation of Demethanizer of BANDAR IMAM Pet. Co.
This project involves the static simulation of the demethanizer using Aspen Plus software for the Imam Khomeini Port Petrochemical Company (BIPC) aimed at separating methane from other gases. The project has been executed for the Imam Khomeini Petrochemical Company, and the license for this unit belongs to Linde.