Introduction
Styrene monomer is an aromatic hydrocarbon that, under normal conditions, is a clear, colorless, and flammable liquid. The conventional method for producing styrene monomer is dehydrogenation after alkylation of benzene with ethylene. Styrene monomer is, in turn, used in the production of styrene-based polymers, which are used in the production of rubber and plastic products, including polystyrene (PS), expanded polystyrene (EPS), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), styrene acrylonitrile, styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), unsaturated resins, and styrene butadiene networks.
A significant amount of styrene monomer is consumed in the production of polystyrene. Generally, polystyrene, whether crystalline polystyrene or high-impact polystyrene, is used in the production of everyday items such as CD cases, cups and disposable tableware, and refrigerator door seals. Expanded polystyrene, as a lightweight foam, is used in house insulation, packaging industries, motorcycle helmet padding and interior car spaces, bridge construction, and movie industry decorations.
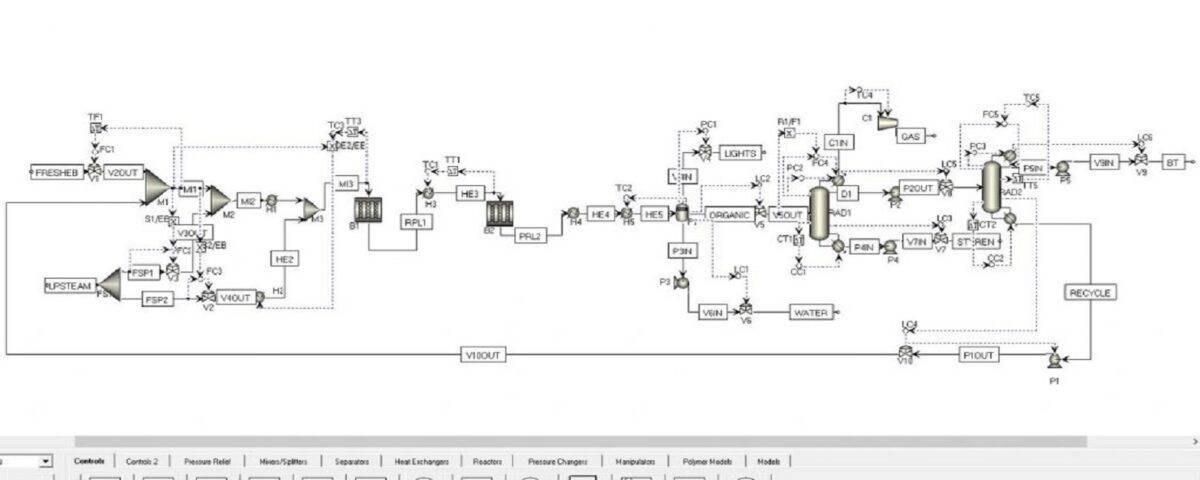
The figure below shows a process flow diagram of a styrene production unit.
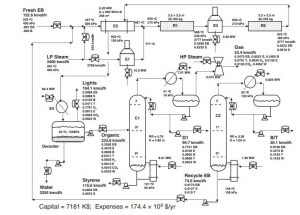
Steady-State and Dynamic Simulation of a Styrene Unit
“In this project, steady-state and dynamic simulations of a styrene unit have been conducted using Aspen Plus software. It’s worth noting that this simulation was based on a chapter from a book. Additionally, this project includes a training video.
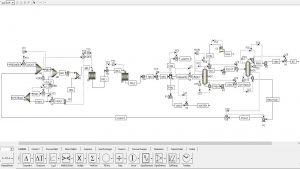
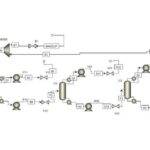
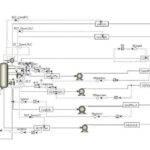
An overview of the steady-state and dynamic simulations is presented in the figures below.
Stable Simulation of Styrene Unit
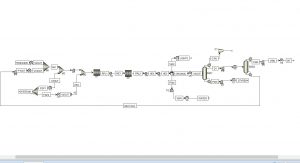
Dynamic Simulation of Styrene Unit