Description
Discontinuous distillation is one of the common methods for separating mixtures. But it is not possible to separate azeotropic mixtures by usual methods. For this purpose, other methods such as adding intermediate materials can be used. This changes the thermodynamic properties and changes the position of the azeotrope points or their removal.
Azeotropic Distillation
This distillation method is usually used in cases where the boiling points of the mixed components are close together. Separation of the initial mixture is possible by adding a special solvent that forms an azeotope with one of the key components. The azeotrope forms the distillation product or residue from the column. And then it separates the solvent and the key component. Often, the adduct forms a low-boiling azeotrope, which is called a brittle azeotrope. Azeotropes often include feed components. But the ratio of key components to other feed components is very different and more.
An example of azeotropic distillation is the use of benzene to completely separate ethanol from water. which forms a low-boiling azeotrope with 95.6 wt% alcohol. A water-alcohol mixture with 95 wt% alcohol is added to the azeotropic distillation column and the benzene-rich stream is introduced from the top. The alcohol residue is almost pure and the upper vapor is a triple azeotrope.
This liquefied steam is divided into two phases. The returned organic layer is sent to the benzene recovery column. All the benzene and the amount of alcohol captured in the upper steam are sent to the first column. The final stream is distilled in the third column to obtain pure water and some double azeotrope.

Simulation of Azeotropic Distillation Tower for Water and Ethanol Separation
In this project, methods of separation of multi-component mixtures that form azeotropes have been investigated. These methods include the use of two distillation towers at different pressures and the use of an extractant to achieve a purity higher than the azeotrope point. The first method is used for mixtures whose azeotrope point composition is sensitive to pressure. If the composition of the azeotrope point does not change significantly with the pressure.
The second method is used. The studied system is ethanol, water and benzene. Ethanol and water form an azeotrope in the composition of 96% by weight of ethanol, and benzene is used as a remover to separate ethanol up to 99.99%. Aspen Plus software has been used in steady state to model this separation unit.
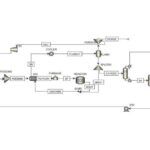
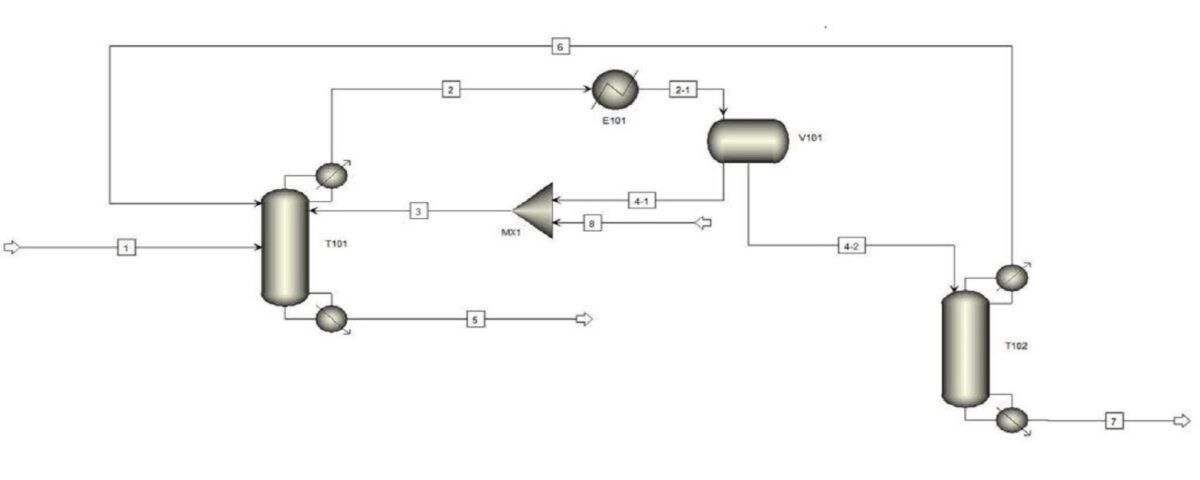
The following figure shows the PFD of the process by which the simulation was carried out.
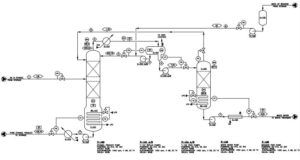
Simulation of Water and Ethanol Azeotropic Distillation Tower
In this project, the simulation of water-ethanol-benzene azeotropic distillation tower with the equation of state NRTL, UNIQUAC and generalized equation of state with data regression has been done in Aspen Plus software. In addition to the simulation files, it also has a complete report and training video.