Description
Benzene, one of the most widely used substances in industry, plays a crucial role in the production of nylon, polystyrene, synthetic rubber, detergents, and many other materials. It is also utilized as a solvent for oils, resins, dyes, plastics, fats, and rubber. Tire and rubber manufacturers, in particular, rely on benzene as a solvent in various stages of production. Major global producers of benzene include the United States, Canada, and Japan.
Benzene is one of the most well-known and intriguing aromatic hydrocarbons, composed of a ring of six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. This project focuses on simulating the production of benzene from toluene.
Benzene Production Processes
- Catalytic Reforming: In this process, a group of hydrocarbons is combined with hydrogen in the presence of platinum chloride at a temperature of 500°C and a pressure of 8-15 atmospheres. After separation, the final product includes benzene.
- Steam Cracking: This method is a suitable way to produce ethylene and other alkenes from linear, large hydrocarbons. Benzene is a byproduct of some of these reactions.
- Toluene Hydrodealkylation: In this process, toluene is converted into benzene. The byproducts of this process are xylene and biphenyl.

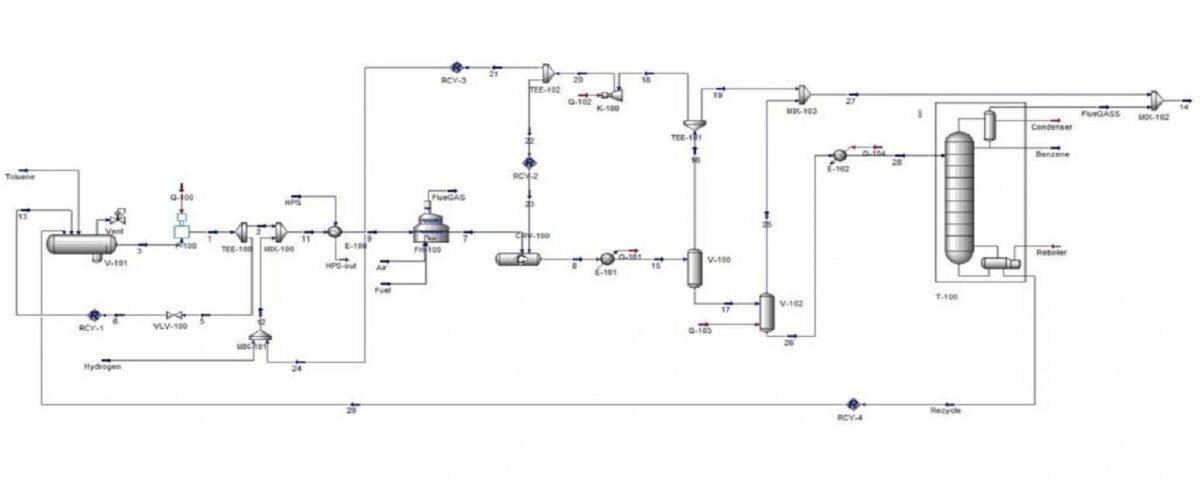
Simulation of The Production Process Benzene From Toluene
Toluene Hydrodealkylation (HDA) is a process used for the production of benzene. The primary reaction in this process is:
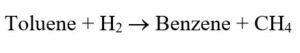
In this new project, the hydrodialkylation of toluene to produce benzene has been simulated with Aspen Hysys software.