Introduction
Ambient air contains 21% oxygen, 78% nitrogen, 0.9% argon and 0.1% rare gases. Meanwhile, the production of high-purity oxygen gas is of particular importance as one of the most important industrial gases that has significant consumption.
Basically, there are two common methods to produce oxygen:
The first production method is deep cooling or so-called cryogenic, which is used for very high purity and production of liquid oxygen.
The second method is pressure swing absorption (PSA), which is a practical method to produce oxygen at the point of consumption.
Description of the Process
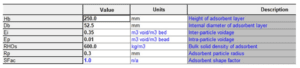
Air enters the oxygen production package at ambient temperature and pressure of 1.4 bar. The air flow rate is 75 liters per minute (equivalent to 0.05 mol per second). In the simulation of this package, only oxygen (21%) and nitrogen (79%) are considered. The oxygen production package includes 2 zeolite beds, 25 cm and 5/25 cm.
The characteristics of the substrate are shown in Figure 1.
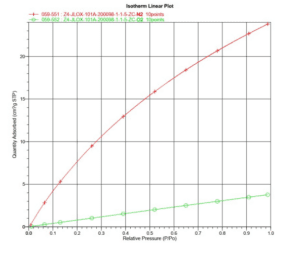
In order to estimate adsorption coefficients, the laboratory results shown in Figure 2 have been used:
How to Calculate Adsorption Coefficients
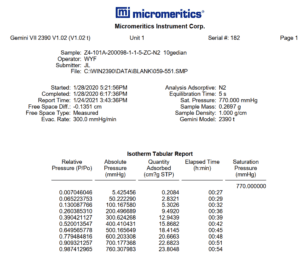
It should be noted that mass transfer coefficients are not known in this system and their values should be determined based on similar systems or changed by trial and error in order to achieve laboratory results.
Also, the adsorption process can be assumed to be at a constant temperature, and due to the low pressure of the system, it can be added from the ideal gas assumption for calculations. Like other PSA packages, this package also includes two substrates, one of which is being absorbed and the other is being regenerated. The absorbents of this package have the ability to absorb nitrogen, therefore, the output of the bed contains rich oxygen.
The duration of the absorption phase is 3.8 seconds. A part of the oxygen coming out of the bed being absorbed is spent on revitalizing another bed. It should be noted that the amount of this current is not known and must be determined by trial and error. The rest of the oxygen flow enters the product tank. This tank initially contains air, and with the introduction of high-purity oxygen, the oxygen concentration in it gradually increases. The volume of the product tank is about 3.6 × 10-4.
After 3.8 seconds, the inlet valve to the first bed is cut off and the inlet valve to the second bed is opened, and again a part of the produced oxygen is used to revive the first bed and the rest enters the product tank. The exhaust gas from the regenerating bed is discharged to the atmosphere.
Laboratory Results
The laboratory results of the device are as follows:
How this Package Works
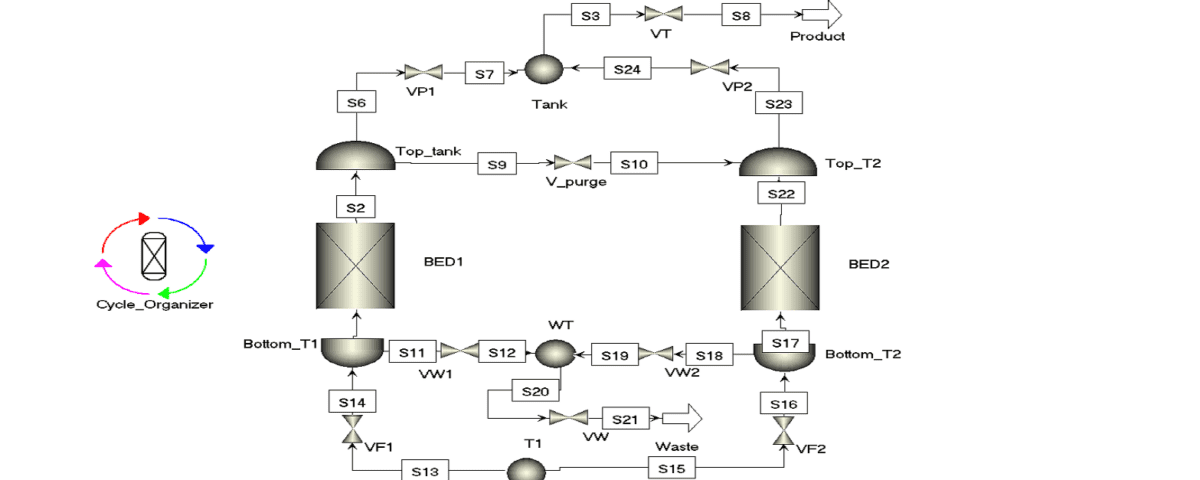
In order to clarify how this package works, pay attention to the following figure:
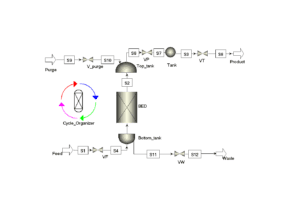
For the simulation of this package, a platform has been used that can obtain the unknown values in the simulation in such a way that its results are consistent with the laboratory results.
Conclusion
The oxygen production technology in this method is the oxygen production system at the place of consumption. Oxygen production in PSA devices is based on the passage of compressed air through different substrates such as artificial zeolite granules, which are called molecular sieves. The nitrogen in the air is trapped in the oxygen generator while passing, and the oxygen in the air is released at low pressure. This generally leads to continuous production of oxygen in the oxygen generator.
Simulation of Oxygen Production Package Process in Aspen Adsim
APIPCO company has simulated the oxygen production package unit in ADSIM software. This project is accompanied by training.