Introduction
Simulation of CO2 Capture Using Enhanced Amines: Most CO2 separation processes rely on physical or chemical absorption of CO2 in a suitable solvent. Physical absorption efficiency is highly dependent on the CO2 concentration in the feed gas. As the CO2 content decreases, so does the absorption rate. This method is ineffective for separating CO2 from air, where concentrations are typically below a few percent. Therefore, chemical absorption of CO2 from air using amine solutions offers higher efficiency and performance.
This project simulates and analyzes the absorption of CO2 using amine solutions, which are commonly employed for chemical CO2 absorption. Furthermore, various promoters, where amine solutions separate CO2 from air in different absorption columns, are investigated. The impact of these promoters on the process is then examined. This project focuses on the removal of carbon dioxide from air. Additionally, the effect of ionic liquids on CO2 absorption by amines is analyzed using simulation.
Ionic Liquids
The unique properties of ionic liquids, such as extremely low vapor pressure (resulting in non-volatility) and the ability to dissolve a wide range of organic, polar, and non-polar substances, make them suitable as clean solvents for separation processes, including gas sweetening. Due to the high solubility of carbon dioxide in ionic liquids, these materials are a promising option for improving the performance of CO2 capture systems.
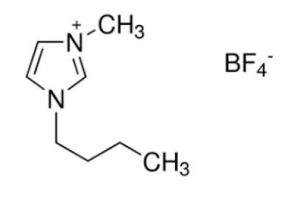
In this research, bmim BF4 was used to enhance the performance of the CO2 capture system with MEA solvent. The molecular structure of bmim BF4 is shown in the figure below.
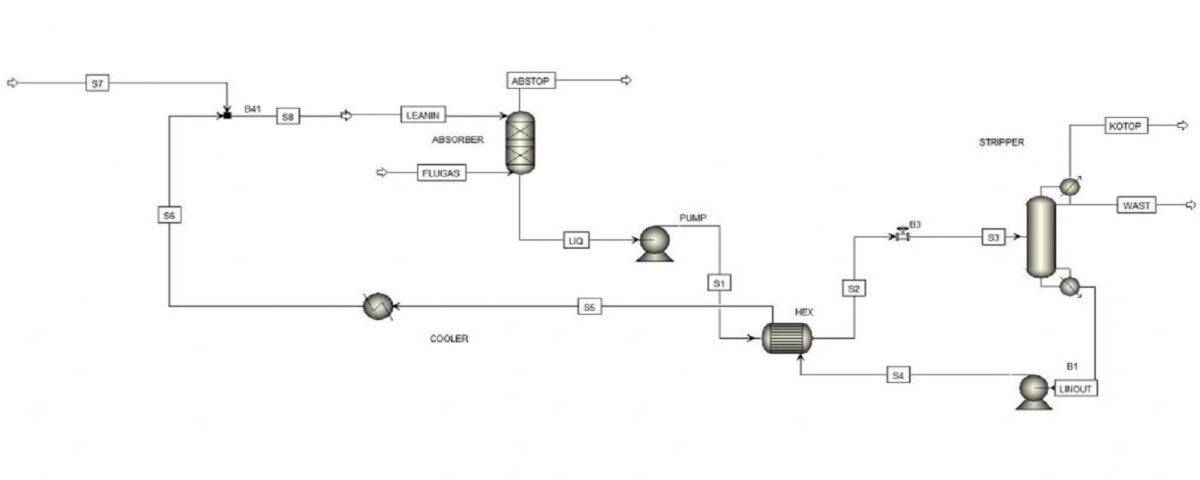
The new process with ionic material is designed as follows.
In this project, the process of absorbing carbon dioxide with the help of upgraded Amine is simulated with Aspen Plus software. Also, the project has a complete report.