Introduction
Petroleum refining is essentially a series of physical and chemical changes applied to the input product of a refinery, which is crude oil, and its conversion into output products or petroleum products and The goal of refining is to transform the low-value and unusable crude oil into high-quality petroleum products that are in demand by the market and consumers.
A refinery is a complex of facilities and equipment that are interconnected and perform the refining process. Refineries vary in type based on their structure and the products they produce. Additionally, each refinery consists of different sections, each with a specific task in the production and improvement of petroleum product quality.

Atmospheric Distillation in a Refinery(CDU)
Crude oil entering a refinery first enters desalting equipment to completely remove the salts contained in it. The crude oil then passes through a number of heat exchangers for preheating. These heat exchangers actually transfer heat from the products produced by the distillation tower to the incoming crude oil. During this heat transfer, the temperature of the crude oil reaches about 280 degrees Celsius. At this stage, the crude oil must be completely heated in a furnace. After exiting the furnace, the temperature of the crude oil reaches about 350 degrees Celsius, and the crude oil is practically in a two-phase state, a combination of liquid and vapor phases.
After reaching the appropriate temperature, the crude oil must enter the distillation tower. The distillation tower is a tall cylinder and consists of a number of trays. The number of trays in an atmospheric distillation tower(CDU) is between 20 and 60. These trays are installed at different heights in the tower, and the oil cuts, depending on their boiling point range between the initial and final boiling points, are collected at their appropriate height and tray and exit. The temperature at the top of the atmospheric distillation tower(CDU) is 70 degrees Celsius and at the bottom is 350 degrees Celsius. Lighter oil cuts are removed from the upper parts of the tower and heavier cuts from the lower parts of the tower. The outlet streams from the distillation tower are in the vapor phase and after passing through the condensers, they become liquid.

Steady-State and Dynamic Simulation of an Atmospheric Distillation Column in a Refinery
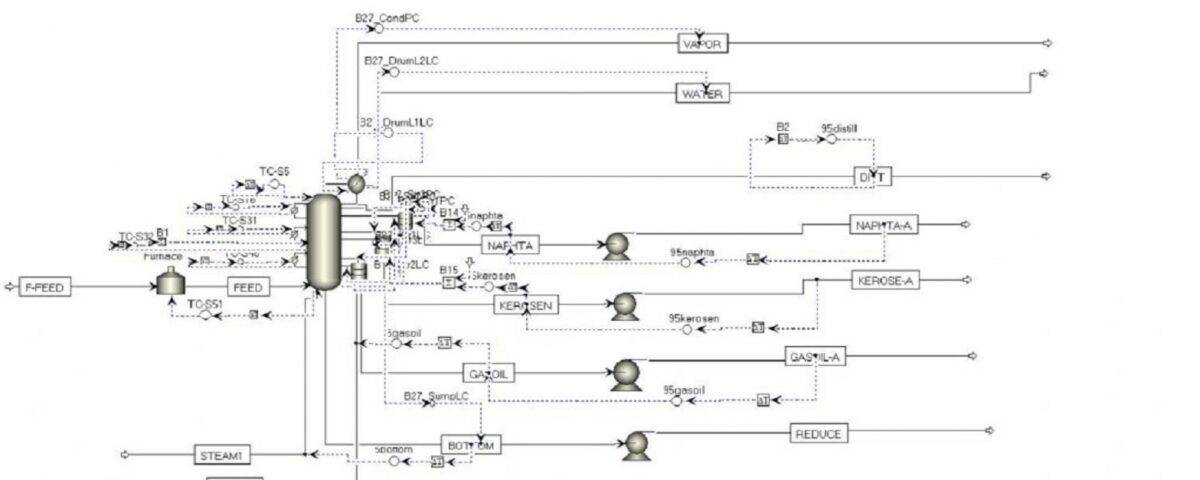
In this project, a steady-state and dynamic simulation of an atmospheric distillation Tower (CDU) in a refinery has been carried out using Aspen Plus software. A schematic of the overall process is shown in the figure below.