Introduction
This report examines and simulates the process of compressing and transporting natural gas through a pipeline using Aspen HYSYS V11.0 software. The main objective of this project is to design an efficient and economical system for transporting natural gas from source to destination, considering technical and economic requirements. Initially, the percentage composition of the input gas is selected based on real data, and an appropriate equation of state for the operational conditions is determined. The compression process is then analyzed using reciprocating compressors and optimizing pipeline design. Finally, an economic analysis is conducted by calculating investment and operational costs to assess the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the system. This report can serve as a practical guide for similar projects in the oil and gas industry.
Simulation Description
This project utilizes Aspen HYSYS V11.0 to simulate the transportation and compression of natural gas. The percentage composition of the natural gas examined is based on data related to the city of Tehran.
Operational Conditions and Equation of State
Due to the high pressure and non-polar hydrocarbon compositions, the Peng-Robinson equation of state is selected for this simulation.
Simulation Steps
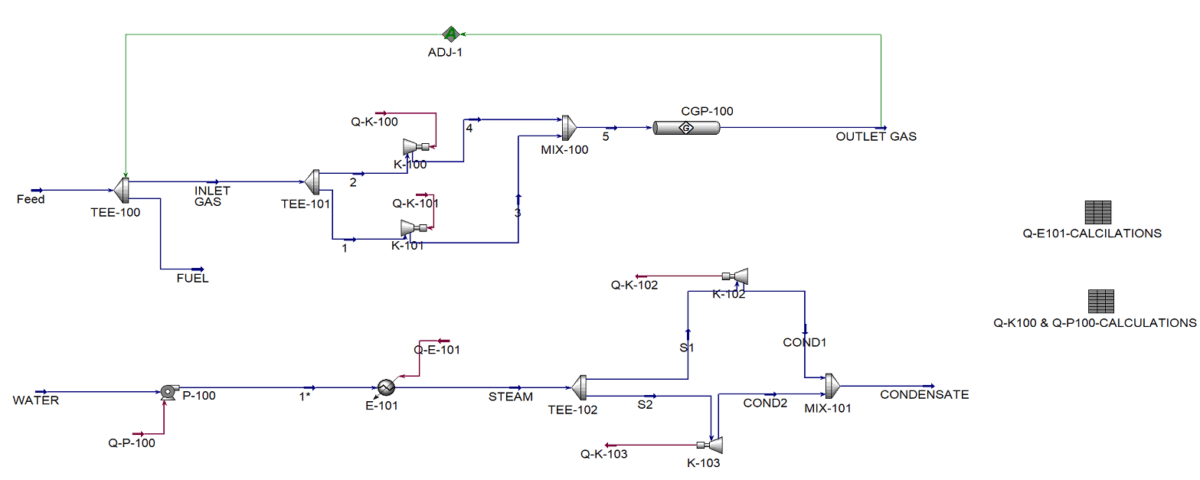
1. Compression: The incoming gas is split into two equal streams in the Tee-101 equipment and enters two similar compressors, K-100 and K-101. After compression, the gas reaches a pressure of 1482 psig and a temperature of 256.9 °F. The compressed gas then enters the CGP-100 pipeline, which is designed with a diameter of 12 inches and made of carbon steel.
2. Fuel Consumption: A portion of the natural gas is used as fuel for generating medium-pressure steam. The generated steam pressure is set at 470.9 psig. Water is pumped to the required pressure in pump P-100 and then converted to steam in boiler E-101. The energy needed for this boiler is supplied by burning part of the gas flow. The boiler efficiency is assumed to be 70%, and the boiler duty is calculated in Q-E-101-CALCULATION.
3. Energy Production for Compressors: The produced steam is split into two parts, supplying the energy required for the compressors and pump P-100 via turbines K-102 and K-103. Calculations related to this part are conducted in Q-K-100 & Q-P-100 CALCULATION.
4. Fuel Adjustment: Using the Adjust tool in the software, the amount of gas used as fuel is set so that the pipeline gas outlet pressure is 1400 psig. Approximately 3.8% of the gas is consumed as fuel.
Economic Assessment
In this project, the economic assessment is based on three main components: compressors, the pipeline, and the steam and electricity generation section, as referenced from the Seider book. The details of each section are as follows:
Compressors
Reciprocating compressors are used based on operational conditions and simulation results. The power consumption of each compressor is estimated at approximately 1627 horsepower. The cost for each compressor is calculated using cost charts in relation to their power and operating pressure:
– Initial Cost: The price of each compressor is estimated at about $1 million based on 2013 data.
– Cost Adjustment: To estimate the price of compressors in 2021, a price index is used. The price index for 2013 was 567, and for 2021, it is reported as 750. Using the following relationship, compressor costs are adjusted to 2021.

Pipeline
The construction and installation costs of the pipeline are a significant portion of this project’s economic assessment. The pipeline is designed from carbon steel with a 12-inch diameter.
– Pipeline Weight Calculation: Considering the external and internal diameters of the pipe as 12.75 inches and 11.37 inches, respectively, the pipe volume is calculated, and from the density of carbon steel (785 kg/m³), the weight is calculated as follows:
– Carbon Steel Volume: Considering the pipeline length (35 miles or about 56.3 km), the required carbon steel volume is 950 m³.
– Pipe Weight: With a density of 785 kg/m³, the total pipe weight will be 745.75 tons.
– Pipeline Cost Estimate: Given an average cost of carbon steel at approximately $900 per ton, the total pipeline cost is estimated at $671,175.
Steam and Electricity Generation Section
The production of medium-pressure steam and energy supply for compressors uses a portion of natural gas as fuel. For calculations in this section, the formula from the reference book is utilized:
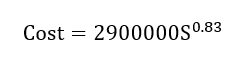
In the above relationship, S is the required power or electricity (MW), estimated at approximately 2.45 MW based on simulation. Thus, the cost for this section is approximately $6.1 million (based on 2013). The mentioned price, similar to the compressor section, would amount to around $8.1 million in 2021.
Summary of Economic Estimation
– Total Compressor Cost: $2.644 million
– Pipeline Cost: $671,175
– Steam and Electricity Generation Cost: $8.1 million
– Total Project Cost: The sum of the estimated costs for this project is approximately $11.4 million in 2021.
This economic analysis indicates that the primary costs are associated with the steam and electricity generation section since it entails the requirements for energy supply for compressors and steam production for the process. Therefore, optimizing energy consumption and equipment operation can help reduce overall project costs.
Conclusion
This project demonstrated that through a comprehensive simulation and accurate economic analysis, optimization of natural gas transportation and compression is achievable. Key factors such as the correct selection of the equation of state, adjusting input flows, and examining various profiles have contributed to performance improvement and cost reduction.
The results indicate that using reciprocating compressors and optimizing pipeline design can facilitate efficient compression and transportation of natural gas. The technical and economic analyses showcase that using appropriate systems for steam production and consuming a portion of gas as fuel can optimize operational costs. Ultimately, considering investment and operational cost estimates, this project proves economically viable and can serve as an effective model for similar projects in the oil and gas industry.
Simulation and Economic Analysis of the Natural Gas Compression Process with Aspen HYSYS
In this project, the simulation and economic analysis of the natural gas compression process has been conducted using Aspen HYSYS version 11.