Introduction
In today’s world, with increasing concerns about climate change and the depletion of fossil energy resources, there has been a significant rise in attention towards renewable energy sources. One renewable energy source that is gaining more and more attention is biomass energy. Biomass encompasses organic materials derived from natural sources such as plants, trees, and agricultural and industrial waste, can be utilized as a sustainable and reliable source for energy production.
Biomass is a fuel derived from organic materials, serving as a renewable and sustainable energy source for generating electricity or other forms of energy. The term biomass includes a wide variety of materials, including wood from various sources, agricultural residues, and animal and human waste. Wood, agricultural by-products, landfill gas, and municipal solid waste are some of the common types of biomass.
Various Methods for Energy Production from Biomass
Energy production from biomass on an industrial scale can be achieved through various methods. Below are some of these methods:
Direct Combustion:
This method involves the direct burning of biomass to produce steam, which is then used to drive steam turbines and generate electricity. It is one of the most common methods for producing energy from biomass.
Gasification:
In this process, biomass is subjected to controlled conditions and high temperatures with limited oxygen to produce combustible gases (such as synthesis gas). This gas can be burned directly or converted into electrical energy.
Biogas Production:
In this method, biomass (especially organic materials) is converted into biogas through biological processes such as fermentation. The produced biogas can be used as fuel for generators or in industrial processes.
Biodiesel Production:
Using chemical processes such as transesterification, vegetable oils or animal fats can be converted into biodiesel. This fuel can serve as a substitute for conventional diesel in engines.
Alcohol Production:
Biomass can be converted into alcohols such as ethanol, which can be used as fuel or as an additive to fossil fuels. This process typically involves the fermentation of the sugars present in biomass.
What Power Can Biomass Produce?
Biomass facilities can generate electricity in a range from 2 to 1000 megawatts. By the end of 2014, Canada had 70 biomass power plants. Collectively, these plants have the capacity to produce 2043 megawatts of electricity. Industries, such as pulp and paper mills, consume approximately two-thirds of this electricity.
The Atikokan Generating Station is the largest 100% biomass power plant in North America. It is located in Northwestern Ontario. Initially, this station generated electricity by burning coal. Following modifications in 2014, it now burns wood pellets. By burning wood pellets, it can produce 205 megawatts of electricity, which is sufficient to power approximately 70,000 homes.
Energy production from biomass as a renewable resource has certain advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
1. Renewability: With proper management, biomass can be sustainably utilized.
2. Reduction of Greenhouse Gases: Burning biomass helps to decrease carbon dioxide emissions.
3. Waste Management: It can contribute to reducing agricultural and industrial waste.
4. Job Creation: It creates job opportunities in agriculture and energy production.
5. Diversity of Energy Sources: It reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
Disadvantages:
1. Pollutant Emissions: Burning biomass may lead to air pollution.
2. High Costs: Initial investment for equipment may be significant.
3. Resource Management Needs: Sustainable production requires careful management.
4. Geographic Limitations: Some regions may lack sufficient resources.
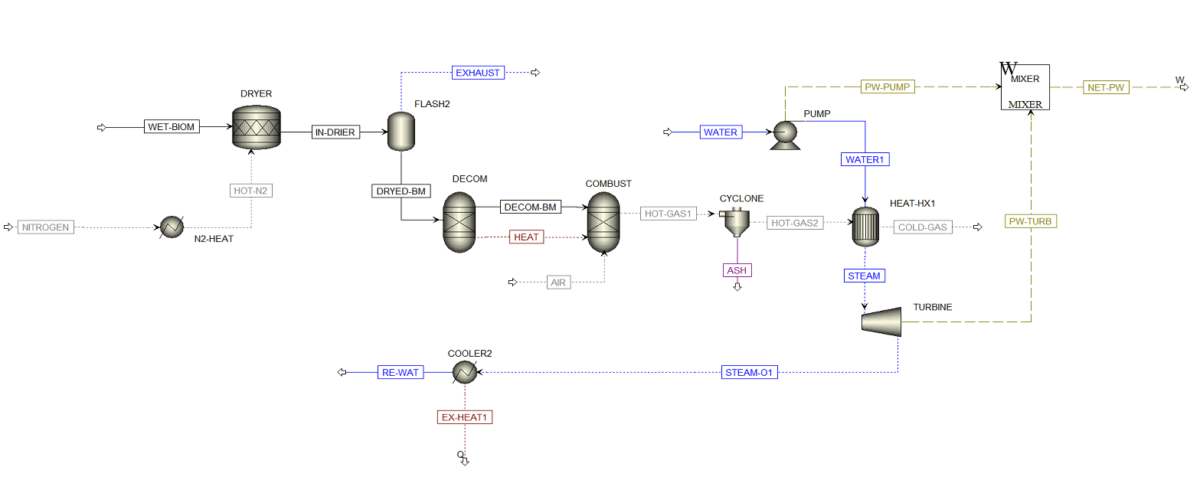
Simulation of Biomass Power Generation Unit:
Simulating a limited-capacity energy production unit using biomass in Aspen Plus software is an effective method for analyzing the performance of renewable energy systems. The following outlines the general steps and important considerations for conducting this simulation:
Simulation Steps
1. Input Definition:
– Select the type of biomass (such as wood, agricultural waste, or other organic materials).
– Determine the physical and chemical characteristics of the biomass, including moisture content, carbon, hydrogen, and ash content.
2. Process Modeling:
– Utilize the available modules in Aspen Plus to model the conversion stages of biomass to energy. These stages may include pyrolysis, gasification, and combustion.
– Choose an appropriate model for each conversion stage, such as chemical and physical models.
3. Capacity Settings:
– Define the energy production capacity of the unit as limited. This can be established as a constraint on the biomass input rate or the energy output capacity.
– Adjust parameters related to system performance under various load conditions.
4. Result Analysis:
– Evaluate the energy production outputs, including the amount of electricity and heat generated.
– Analyze energy efficiency and assess the impacts of various factors on system performance.
5. Optimization:
– Employ optimization techniques to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. This may involve adjustments to input ratios, temperature, and process pressure.
Key Considerations:
– Chemical Selection: Ensure the correct choice of chemicals for the simulation processes.
– Accurate Modeling: Utilize empirical data and validated models to enhance the accuracy of the simulation.
– Sensitivity Analysis: Investigate how variations in inputs affect outputs and system efficiency.
– Waste Management: Consider strategies for managing waste generated from the process.
Simulating a limited-capacity energy production unit using biomass in Aspen Plus can assist in identifying challenges and opportunities within this field, leading to optimized decision-making in the development of renewable energy projects.
Examples of Projects Completed by Anil Pars Process Industry Company
Feasibility Study and Simulation of Bio-Oil Production from Bagasse with Aspen Plus
Simulation of Sesame Stem Bio-Oil Production From Biomass Pyrolysis With Aspen Hysys
The Anil Pars Process Industry Company proudly announces its capability to execute industrial-scale energy production simulation projects using biomass methods. Leveraging our technical expertise and extensive experience in this field, we have successfully implemented numerous diverse projects focused on sustainable energy production.
Our experience encompasses the design and implementation of complex biomass-to-energy conversion systems, process optimization, and performance evaluation of these systems. These projects have not only contributed to increased efficiency and reduced costs but have also led to the development of innovative and sustainable solutions in the realm of renewable energy.
Simulation and Optimization of Power Production From Biomass
In this project, the simulation and optimization of energy production from biomass methods have been carried out using ASPEN Plus software.