Introduction
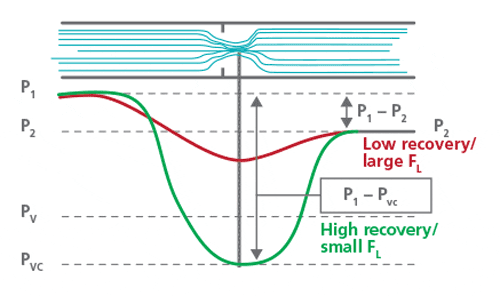
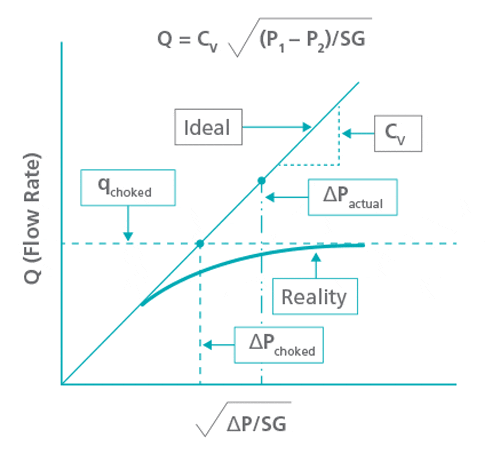
Choked Flow is one of the key phenomena in industrial systems and chemical processes that occurs when a compressible fluid passes through a nozzle, orifice or any other restriction. Under normal conditions, the fluid flow rate is proportional to the pressure difference between the upstream and downstream of the flow. In other words, the greater the pressure difference. Flow also increases. But when the speed of the fluid reaches the speed of sound at the bottleneck (limiting) point. The phenomenon of Choked Flow occurs.
In this condition, a further decrease in downstream pressure cannot increase the mass flow rate and the flow remains constant at this point. This happens because the fluid speed has reached the speed of sound and pressure changes downstream will no longer affect the flow. In this case, the Mach Number in the throat is equal to one, while in the critical flow, the Froude Number is equal to one. Therefore, the two phenomena are not technically the same.
Choked Flow is of particular importance in the design and optimization of industrial systems. Failure to properly understand this phenomenon can lead to incorrect design of equipment and reduce the performance and safety of the system. For example, in the process of transferring gases or liquids under pressure, failure to correctly predict choking conditions can cause problems such as equipment damage, reduced efficiency, and even safety risks.
Description of The Process
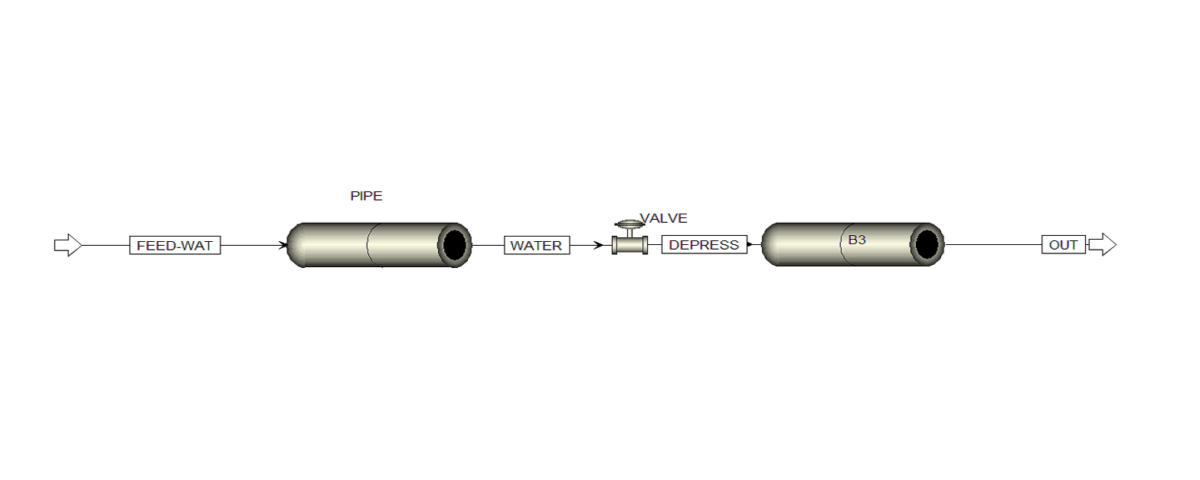
In this project, water flows at a pressure of 50 psig, a temperature of 290 F, and a flow rate of 6000 lb/hr through a 4-inch pipe. In the path of this flow, a 3-inch valve is placed, from which the output flow enters the 4-inch pipe with a pressure of 41 psig. Purpose of the simulation is to determine the outlet pressure at which the choke phenomenon occurs.
The calculations related to the flow in the choking state and investigation of the critical conditions were performed using Aspen Plus software, and training of the simulation steps is also available in the report.
Conclusion
The results of this project indicate the occurrence of Choked Flow phenomenon in certain conditions of outlet pressure. So that after this point, the flow rate remains constant and the pressure drop in the downstream has no effect on the flow increase.
By using simulation performed in Aspen Plus software, students and engineers. can learn about the Choked Flow process and analyze critical conditions of this phenomenon in industrial systems. As an applied study, this project provides an opportunity to learn and gain a deeper understanding of the concepts of flow choke and its impact on the design and performance of fluid transmission systems.
Simulation and Analysis of Choked Flow With Aspen Plus
This student project deals with the simulation of compressible fluid flow through a valve and pipe using Aspen Plus software. The purpose of this simulation is to investigate the phenomenon (Choked Flow) and determine the outlet pressure at which the choke phenomenon occurs. In addition, the project includes training and detailed explanations to better understand the simulation process and analyze the results.