Introduction
Total base number (TBN) boosters are chemical additives used in lubricants to increase their alkaline properties. The main purpose of these additives is to neutralize acid by-products that are created during fuel combustion. Therefore, they protect engine components against corrosion and wear. This plan outlines the technical knowledge required to understand, implement and optimize the use of TBN amplifiers in various applications.
Total Base Number (TBN)
A measure of the alkalinity of a lubricant, which indicates its ability to neutralize acids. High levels of TBN ensure long-term protection against corrosion and wear. The key components of TBN are detergents, dispersants and excessive additives. Its common chemicals are calcium sulfonate, magnesium sulfonate, and barium sulfonate.
TBN boosters react with acidic compounds to form neutral salts that are less damaging to engine components. TBN boosters help keep engine surfaces clean by preventing scale formation. By neutralizing harmful acids, it increases the life of the engine. By maintaining the effectiveness of the lubricant, it reduces the frequency of oil changes. It maintains optimal engine performance by preventing corrosion and deposit accumulation.
The Primary Objective of The TBN BOOSTER:
– Increase the technical capabilities of our team.
– Ensuring alignment with industry standards and best practices.
– Foster a culture of learning and continuous improvement.
– Equipping the team with the necessary skills to efficiently manage current and future projects.
– Identify the gap between existing skills and required skills.
– Analyze survey results to prioritize areas that need improvement.
– Set skill levels: beginner, intermediate, advanced.
The TBN BOOSTER know-how initiative is a strategic initiative to enhance the technical skills of our team and ensure we remain competitive in a rapidly evolving technology landscape. By investing in continuous learning and development, we can drive innovation. Improve project results and achieve our organizational goals.
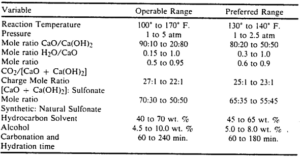
The Process for The Preparation of Calcium Sulfonate has Been Improved
The present invention provides a novel and efficient method for the production of excess calcium sulfonates with very high base open number (TBN). These additives are used as acid neutralizers in lubricating oils, especially in marine diesel engines. They play an important role in protecting engine parts against corrosion and sludge formation.
Due to the increasing demand for higher performance oils, the need for sulfonates with TBN higher than 500 has also increased. Conventional methods of producing these additives have faced limitations and have not been able to produce products with this level of alkalinity. The present invention overcomes this limitation by improving the production process and produces a product with low viscosity and high compatibility with base oil. At the same time, it provides effective protection for marine diesel engines.
By providing an innovative solution for the production of excess calcium sulfonates with high TBN, the present initiative has taken an important step towards improving the performance and extending the life of marine diesel engines. This product, having many advantages, has a high potential for commercialization and wide application in various industries.
Sulfonates
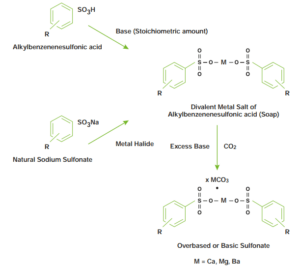
Sulfonate cleaning additives are metal salts of organic acids. The acids used in making these additives are aryl sulfonic acids such as alkylbenzene sulfonic acid, carboxylic acids, etc.
As a result of the reaction between these acids and mineral bases such as metal oxides, hydroxides and carbonates, salt is formed. As mentioned before, these types of cleaners also include neutral or overactive sulfonates. Among metal sulfonates, calcium, magnesium, and barium sulfonates are common. The performance of a sulfonate depends on several factors that change according to its application. The production process of sulfonate cleaners is as follows.

Phenates
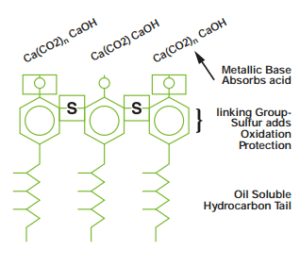
Phenates are formed from the reaction of alkylated phenols with sulfur-containing compounds, followed by neutralization with metallic oxides or calcium, magnesium, or barium hydroxides. The chemical structure of phenates consists of four components:
Hydrocarbon tail
Connected groups
Metal carbonates
Sulfur
The first part of these cleaning additives that makes it possible to dissolve Phenates in lubricating oils is its hydrocarbon tail. This part is formed from the polymerization of low molecular weight hydrocarbons such as propylene, which usually contains 12 to 15 carbons.
The second part is connecting groups that connect long hydrocarbon tails to metal salts or carbonates, which in the case of these types of additives are phenols. Connecting groups and hydrocarbon tails react together and create alkylphenol. which react with sulfur, metal oxides and carbon dioxide and in the presence of glycol catalyst, phenates are produced.
The third part is metal carbonate and the fourth part is sulfur, which connect phenates to each other and to larger polymer molecules. At ambient temperature, phenates have high viscosity, are insoluble in water and are almost black liquid with special smell. The sulfur present in these additives has created the property of preventing oxidation. And it prevents the increase in oil viscosity caused by the process of oxidation and polymerization. According to the mentioned features, Phenates cleaners have antioxidant properties in addition to cleaning properties. Among the phenates, calcium phenate is the most widely used, especially in the formulation of marine oils.
Super Alkaline Calcium Sulfonate Oil (TBN Booster)
This product is used as one of the most important additives to car engine oil. And its task is to neutralize the acids resulting from combustion due to the sulfur present in the gasoline, which causes no corrosion in the engine cylinder wall. The product is a multi-purpose super alkaline super sulfonate based on calcium. which is generally used as a cleaner and anti-corrosion in the formulation of all engine oils. Applications of this additive include oil for gasoline cars, diesel cars, marine oils, railway diesel engines and other internal combustion engines.

TBN Additives
Additive TBN (Total Base Number) in lubricating oils plays an important role in maintaining the properties of the oil and protecting the engine and equipment. TBN measures the amount of base (recycling acids) in an oil. It shows the oil’s ability to neutralize acids produced during engine operation. These additives help prevent corrosion and rusting of engine parts and increase the useful life of the oil.
Lubricant additives are used to improve the performance of lubricating oils. These additives can perform a variety of functions including reducing friction, preventing wear, protecting against rust and corrosion, improving viscosity index, and preventing the formation of sludge and deposits.
TBN (Total Base Number) is a measure that shows the alkalinity of engine oil. And it is used as an important indicator to determine the capacity of oil in neutralizing acids. Acids can form over time as a result of fuel combustion and thermal breakdown of oil in the engine. TBN additives are mainly composed of alkaline compounds such as detergents and anti-corrosion agents that help protect the engine from corrosion and rust. Detergents are usually calcium, magnesium, or sodium based and help keep engine parts clean.
Conclusion
Understanding and effectively using TBN boosters is critical to maintaining engine health and optimizing lubricant performance. This scheme provides a comprehensive guide to the technical aspects of TBN amplifiers. which enables informed decision making and best practices in various applications.
Providing Design and Technical Knowledge of TBN BOOSTER
In this project, design and technical knowledge of TBN BOOSTER has been done.