Introduction
Post-combustion carbon capture (PCC) has gained significant attention as a pivotal technology for mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and addressing climate change. HYSYS simulations, as a powerful tool in this domain, empower engineers to study, optimize, and design more efficient PCC systems. The emission of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide (CO₂), is recognized as one of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time. PCC, a process designed to capture CO₂ from flue gases of power plants and other emission sources, plays a critical role in reducing this pollutant. HYSYS simulations, by providing accurate thermodynamic and kinetic models, enable engineers to gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms governing PCC processes and predict system performance under various operating conditions.
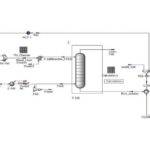
Simulation Steps:
Fluid Stream Definition
Flue gas is defined as a non-ideal fluid with specified components or an appropriate equation of state. The absorbent solution (typically an amine solution) is also defined as a non-ideal fluid. Fluid flow simulation in HYSYS is based on the governing equations of fluid mechanics and thermodynamics. These equations include mass conservation, momentum conservation, and energy balance. HYSYS uses these equations to predict fluid behavior under various conditions, such as flow in pipes, heat exchangers, distillation columns, and reactors.
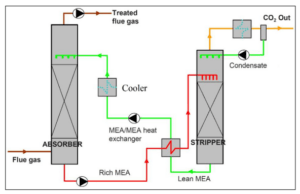
Absorption Column Simulation
The absorption column is modeled in HYSYS with its geometric specifications (height, diameter) and type (tray or packed bed). The inputs (flue gas stream, absorbent solution stream) and outputs (treated gas stream, CO2-rich solvent stream) are specified. Thermodynamic equilibrium equations for the CO2-amine solution absorption system are defined. The thermodynamic properties of fluids are determined using HYSYS libraries or custom thermodynamic correlations.
Regeneration Column Simulation
The regeneration column is simulated to concentrate the absorbed CO2 and regenerate the absorbent. The specifications of the regeneration column (type, dimensions) and inputs/outputs (CO2-rich solvent stream, steam/heat stream, product streams) are defined. Operating conditions (pressure, temperature, flow rate) are determined. The regeneration column is a key separation unit in the natural gas sweetening process using amine absorbents. HYSYS simulation provides a powerful tool for modeling and analyzing the performance of this column to optimize the process and reduce costs. In HYSYS simulation, the regeneration column is modeled as a multi-stage absorption column with different input and output streams. Thermodynamic and kinetic equations in HYSYS are used to calculate vapor-liquid equilibrium, mass transfer between phases, and concentration profiles along the column.
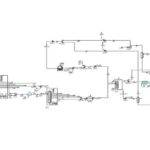
Column Connection
Column connection in simulation involves modeling the behavior of transmission towers or similar structures under various conditions. These simulations can be used to evaluate the stability and performance of the towers under different loads such as wind, snow, ice, earthquakes, and explosive loads. The absorption and regeneration columns are connected with appropriate fluid streams. Boundary conditions between the two columns are properly defined.
Simulation and Analysis
Aspen HYSYS, as an advanced tool for process simulation and modeling, plays a pivotal role in the design, analysis, and optimization of chemical processes. Widely used in the oil, gas, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and food industries, this software enables chemical engineers to gain a deeper understanding of system performance through accurate simulation and comprehensive analysis, leading to more efficient and economical designs. Simulation conditions (pressure, temperature, flow rate) are specified for both columns. The simulation is run, and the results are analyzed, including: CO2 absorption and concentration rates, fluid stream properties in each column, energy requirements and heat load, and the performance of separation units.
Review and Optimization
The goal of the optimization phase is to improve the performance of the simulated process. This is achieved by adjusting process variables such as pressure, temperature, flow rate, and catalyst type to achieve desired results, such as increased product yield, reduced energy consumption, or minimized operating costs. Simulation results are reviewed, and parameters are adjusted as needed. Optimizations are performed to improve process performance, including operating conditions, absorbent type, and column configuration.
Advantages of HYSYS Simulation:
Deeper Process Understanding
One of the primary benefits of using Aspen HYSYS for simulating chemical processes is the deeper understanding it provides of process behavior. By creating a detailed computer model of a real-world process, engineers can predict and analyze system behavior under various operating conditions. In the case of CO2 capture processes (PCC), HYSYS simulations aid engineers in fully comprehending the factors influencing CO2 absorption and sorbent regeneration.
Process Optimization
In today’s competitive landscape, industries are increasingly seeking ways to optimize their processes and gain a competitive edge. HYSYS, as a powerful tool, enables chemical engineers to create accurate models of complex processes, identify system bottlenecks and weaknesses, and develop effective solutions. By simulating PCC processes in HYSYS, process parameters such as flow rate, temperature, and pressure can be optimally adjusted to achieve maximum CO2 capture efficiency and minimal energy consumption.
Cost Reduction
Aspen HYSYS, as an advanced process simulation tool, plays a crucial role in reducing costs and enhancing efficiency and profitability across various industries. This is achieved by providing valuable insights during the early stages of project design and throughout ongoing operations. Optimizing PCC processes using HYSYS simulations can lead to significant reductions in both operating and capital costs over the long term.
Applications of HYSYS Simulation
- Sorbent Selection: Choosing the appropriate sorbent in HYSYS simulations is critical for achieving an efficient and economical process. This complex selection involves carefully considering various factors and conducting detailed simulations. Selecting a suitable sorbent with high absorption capacity, rapid reaction rate, and good thermal stability can be accomplished through HYSYS simulations.
- Design of Absorption and Regeneration Towers: HYSYS is widely used for designing and simulating absorption and regeneration towers in the chemical engineering field. This software enables engineers and process designers to predict and optimize the performance of these towers under various operating conditions. HYSYS is used to determine the optimal dimensions and configuration of absorption and regeneration towers to achieve maximum CO2 capture efficiency and minimal pressure drop.
- Energy Consumption Optimization: Identifying and eliminating energy losses in PCC processes using HYSYS simulations leads to significant reductions in energy consumption and operating costs.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: HYSYS is an effective tool for assessing pollutant emissions, water consumption, and other environmental impacts associated with PCC processes.
Conclusion
Aspen HYSYS, as a powerful tool in the study, optimization, and design of PCC systems, plays a pivotal role in the development of more efficient and cost-effective CO2 capture technologies. By overcoming the challenges associated with this method, Aspen HYSYS can be effectively employed as a tool to address environmental challenges arising from greenhouse gas emissions and to advance sustainable development goals.
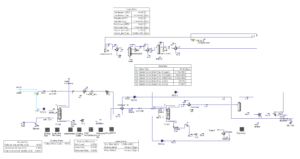
Post Combustion CO2 Capture Simulation with Aspen HYSYS
In this project, the post-combustion CO2 capture process has been simulated using Aspen HYSYS version 14.