Introduction
Aniline production from Phenol and Ammonia is a highly significant industrial chemical process. Aniline serves as a fundamental building block in the manufacturing of a wide array of products, including dyes, pharmaceuticals, and other chemicals. The overall production process of aniline typically involves the following steps:
Feedstock: The feedstock for this process comprises phenol and Ammonia. Phenol purity should be at least 93%, and ammonia purity must exceed 99%.
Mixing: Phenol and Ammonia are mixed in stoichiometric proportions within a mixer.
Reaction: The phenol-ammonia mixture is converted into Aniline and water within a reactor under suitable temperature and pressure conditions.
The primary reaction proceeds in two stages:
- Stage 1: Phenol and Ammonia react to form aniline and initial water (Aniline water).
- Stage 2: Aniline and initial water react further to form aniline and secondary water (Aniline oil).
Separation: Aniline is separated from water. Various methods can be employed for this separation, including distillation, liquid-liquid extraction, and evaporation-distillation. Purification: Crude aniline is refined to achieve the desired purity (exceeding 99%). Several purification methods can be used, such as distillation, crystallization, and adsorption.
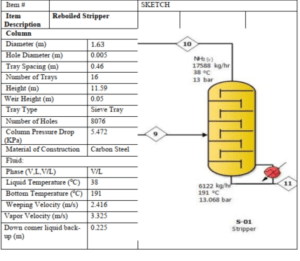
Stripper Column
The accompanying diagram illustrates a stripper column. A stripper column is a device used to separate vaporized components from a liquid. It finds extensive application in various industries, including chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing.
Stripper Column Operation
Liquid at 91°C enters the stripper column from the bottom and is pumped upwards. Vapor at 191°C enters the column from the top. The vapor travels downward through 8076 holes, each with a diameter of 0.005 meters, located on each tray, coming into contact with the liquid. During this contact, the vapor absorbs certain components from the liquid, while the liquid absorbs components from the vapor. The liquid, enriched with vapor components, exits the column from the bottom at 191°C, and the vapor, enriched with liquid components, exits from the top at 91°C.
Reactor Specifications
- Name: Aniline Reactor
- Diameter: 0.76 meters
- Height: 3.1 meters
- Volume: 1.5 cubic meters
- Material: Low-alloy steel
- Type: Vertical reactor
- Operating Pressure: 16 bar
- Pressure Drop: Minimum 0.2 to maximum 0.38 kPa
- Catalyst Type: Silica alumina
Tubular reactors are a type of reactor used for a wide range of chemical processes. They are known for their high efficiency, flexibility, and scalability. However, they can be complex, sensitive, and unsuitable for certain processes.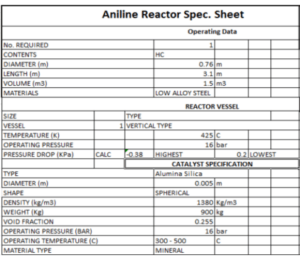
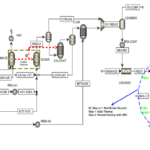
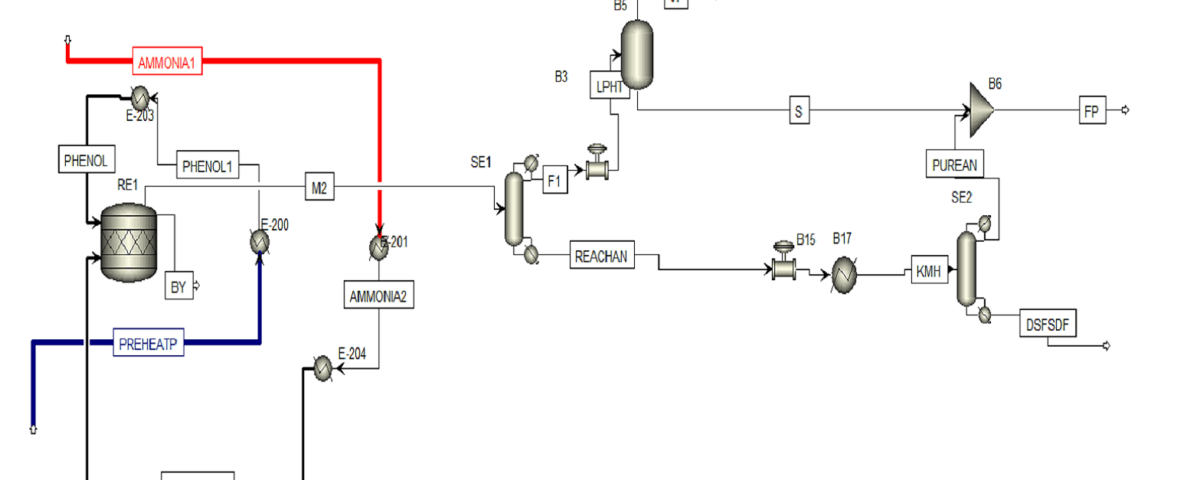
The diagram below shows the simulation of aniline production process by phenol amination method, which was done using Aspen HYSYS software. This simulation includes different process steps, including feed preparation, amination reaction, separation of products, purification of aniline and recycling of gases. This simulation can be used to investigate the effect of process parameters, design and optimization of aniline production unit and train operators.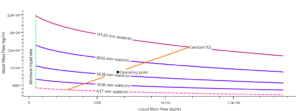
Conclusion
Simulation is a powerful tool for designing, analyzing, and optimizing aniline production units using the phenol amination process. For more accurate simulations of the aniline production process, more precise thermodynamic models and complex kinetic equations can be used. Simulation can be used to investigate various operating scenarios and optimize energy consumption in aniline production units. Simulation results can be used to justify the feasibility Study of aniline production projects.
Conceptual Simulation of an Aniline Production Unit Using the Phenol Amination Process
In this project, the aniline synthesis process has been simulated using Aspen Plus version 14. A complete report (in PDF format only) is available for this project.