Introduction
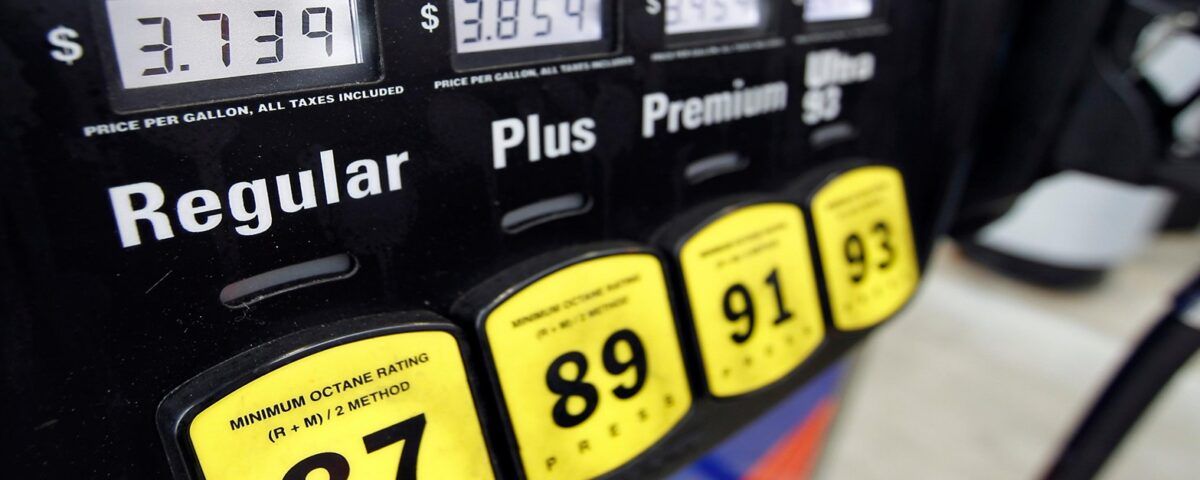
The optimization of the fuel production process with 93 octane at Damun Petrochemical is significant from various aspects. The main goals of this optimization include increasing fuel quality, reducing production costs, improving energy efficiency, and minimizing environmental pollution. Octane is an indicator of a fuel’s resistance to knocking. Fuels with higher octane ratings demonstrate greater resistance to knocking and help prevent the phenomenon of “knocking” in engines. This leads to enhanced engine performance, reduced fuel consumption, and lowered emissions.
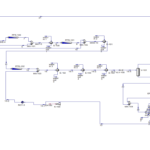
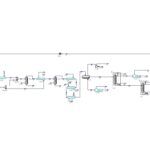
Process Description
Optimizing the production of 93 octane fuel in a petrochemical complex involves several key processes and strategies:
1. Raw Material Selection and Preparation: This process begins with selecting high-quality raw materials, such as specific fractions of crude oil or starting formats. These are treated to remove impurities and adjust the composition to achieve the desired octane rating.
2. Reforming and Upgrading: Catalytic reforming or hydrocracking processes are used to convert low-octane hydrocarbons into high-octane components. The reforming process involves heating the raw material in the presence of a catalyst to increase the octane number by restructuring the molecular structure.
3. Blending: High-octane components produced during the reforming process are blended with other hydrocarbons to achieve the final 93 octane rating. The blending process must be carefully controlled to ensure that the desired octane level is reached without compromising other fuel properties.
4. Quality Control and Testing: Regular testing and quality control throughout the production process ensure that the fuel meets the 93 octane specifications. This includes laboratory analysis of samples to measure octane rating, volatility, and other relevant characteristics.
5. Process Optimization: Optimization involves adjusting process parameters such as temperature, pressure, and catalyst activity to maximize yield and efficiency. Advanced control systems and real-time data analysis assist in fine-tuning these parameters for optimal performance.
6. Minimizing Waste and Energy Efficiency: Implementing strategies to minimize waste and enhance energy efficiency, such as recovering by-products and heat recovery, is essential. This reduces operational costs and environmental impacts.
7. Regulatory Compliance and Safety: Ensuring that the production process complies with environmental regulations and safety standards is crucial. This includes monitoring emissions, managing hazardous materials, and maintaining equipment to prevent incidents.
By following these steps, the production of 93 octane fuel can be optimized to achieve high quality and efficiency while meeting regulatory and economic requirements.
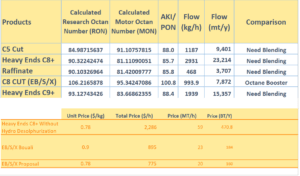
Conclusion
The present study aims to provide a comprehensive, evidence-based approach to optimizing the 93 octane fuel production process at Damun Petrochemical. Increasing the octane rating of the fuel not only improves engine performance and reduces fuel consumption but also leads to lower emissions and better compliance with environmental standards.
Optimizing Fuel Production Scenario with 93 Octane at Damun Petrochemical
In this project, optimization of 93 octane fuel production scenario has been done in Damun Petrochemical.