Introduction
COMSOL Multiphysics is a powerful software for simulating various physical phenomena, including fluid flow, heat transfer, and chemical reactions. One of its significant applications is in simulating mixers. Mixers are devices used to blend different substances and find extensive use in industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals.
Mixer Simulation in Comsol
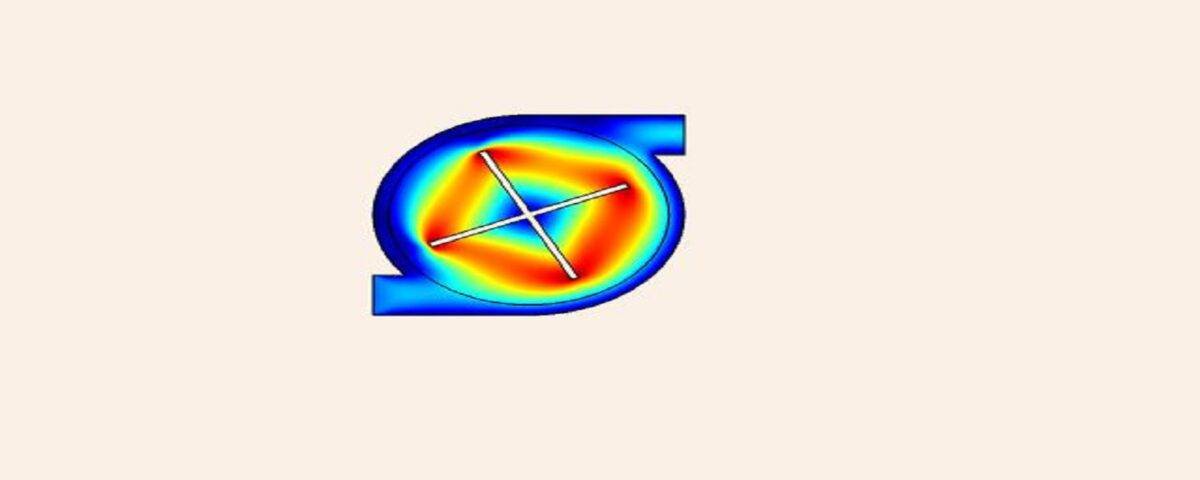
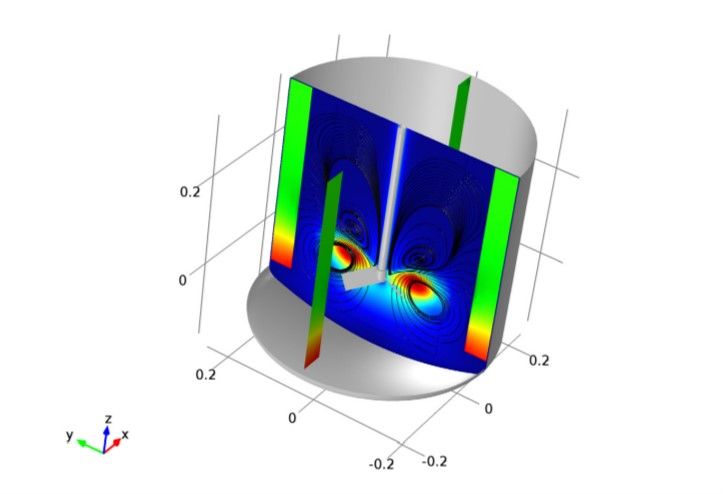
Mixers are made in two types: dynamic and static. In static mixers, flow turbulence is used, and in dynamic mixers, rotating blades are used for mixing. In this project, we will simulate and analyze the fluid flow inside a mixer with the help of Comsol software. The method of mixing the selected fluid inside a dynamic mixer has been investigated. To simulate the movement of particles, Fluid Flow physics is used, and to model the movement of rotating blades, Rotating Machinery physics is used, and the geometry is assumed to be two-dimensional.
Steps for Simulating a Mixer in COMSOL
- Geometry Creation: Construct the mixer’s geometry using COMSOL’s drawing tools. (For simplicity, let’s assume a 2D geometry.)
- Physics Definition: Select the necessary physics for the simulation. For mixers, fluid flow physics is typically employed. (To simulate particle motion, use Fluid Flow physics, and for rotating blades, employ the Rotating Machinery physics.)
- Material Definition: Define the properties of the fluids involved in the mixing process.
- Boundary Condition Definition: Specify appropriate boundary conditions for the model. For instance, you can define inlet velocity, outlet pressure, and slip or no-slip conditions.
- Meshing: Generate a mesh for the model. Mesh density depends on the model’s size and the complexity of the flow.
- Equation Solving: Solve the governing equations for fluid flow.
- Result Analysis: Analyze the simulation results and extract desired parameters.