Introduction
Packed bed are fundamental components in numerous industrial processes. These beds consist of solid particles (which can be made of various materials like metal, ceramics, or polymers, depending on the process) contained within a vessel. A fluid (gas or liquid) passes through these particles, interacting with them to facilitate mass or heat transfer.
Types of Packed Beds
Packed beds can be categorized based on several parameters:
- Fixed bed: In this type, the solid particles are stationary, and the fluid flows through them.
- Moving bed: In this type, the solid particles are continuously in motion (like fluidized beds).
Types of Particles and Packing Materials
- Particle size
The choice of particle size depends on the process. Fine particles are suitable for processes like adsorption and ion exchange that require a high surface area. Conversely, larger particles are used for catalytic processes that require more void space for fluid flow. - Packing material
Packing materials can be categorized into three types based on their function:
- Adsorbents: Such as zeolites, used to adsorb specific molecules from the fluid.
- Catalysts: Used to accelerate chemical reactions.
- Inert packing: Like sand, used to create void space and improve fluid distribution.
Wide-Ranging Applications of Packed Beds
Packed beds find applications in various industries:
- Oil and gas: For dehydrating natural gas, sweetening gas, and catalyzing chemical reactions in refineries.
- Chemical industry: In distillation processes, adsorption of various substances, and ion exchange for separating chemical compounds.
- Pharmaceutical industry: For water purification, separating active pharmaceutical ingredients, and manufacturing various drugs.
- Food industry: For water purification, filtering oils, and separating impurities from food products.
How They Work
When a fluid passes through a packed bed, several physical phenomena occur:
- Adsorption: Fluid molecules adhere to the surface of the solid particles.
- Ion exchange: Ions in the fluid exchange with ions on the surface of the solid particles.
- Chemical reactions: In the presence of a catalyst, chemical reactions occur between the fluid molecules and the surface of the solid particles.
- Heat transfer: Heat is exchanged between the fluid and the solid particles.
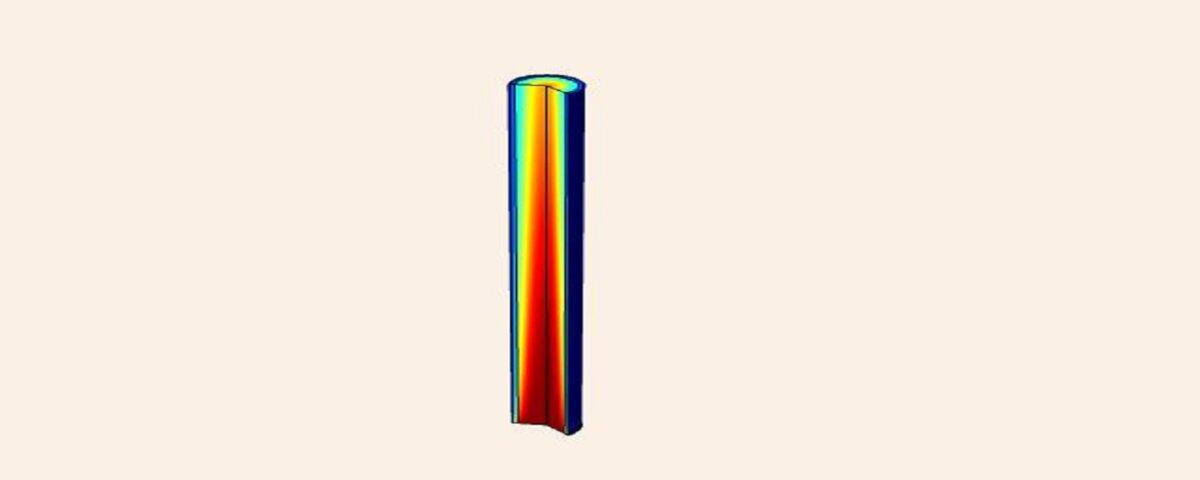
Packed beds have long been employed in various separation processes owing to their high mass transfer surface area, extended phase contact time, low pressure drop, and reduced flooding and liquid entrainment. In this study, mass transfer within a packed bed reactor for formaldehyde production is investigated using COMSOL Multiphysics. Simulation results are presented.

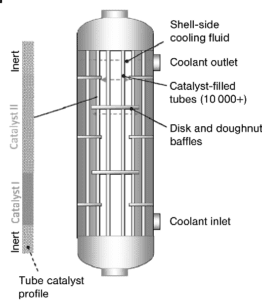
The figure below shows the schematic view of the formaldehyde production reactor.