Introduction
Simulation of two-phase flows in pipes is one of the important topics in engineering sciences and various industries. Especially in the oil and gas, chemical and pharmaceutical industries. This type of simulation allows us to do this. to investigate the interaction and mixing of the two liquid and gas phases inside the pipes.
The particle dynamics model (DEM) is especially important in simulating the movement of particles in two-phase flows. This model allows us to observe the changes and interactions of the physical and dynamic details of the particles during the flow process. In mixing tubes, these interactions can have a significant effect on mixing efficiency and mass transfer.
In this research, an attempt is made to accurately analyze the two-phase flow in a mixing tube by using FLUENT simulation capabilities and DEM model. This parallelism between physical models and numerical simulations allows a deeper understanding of mixing and dispersion processes. And it can help to optimize industrial processes. Specifically, the aim of this study will be to investigate the effect of different parameters such as flow rate, pipe diameter and physical characteristics of phases on mixing efficiency.
Process Description
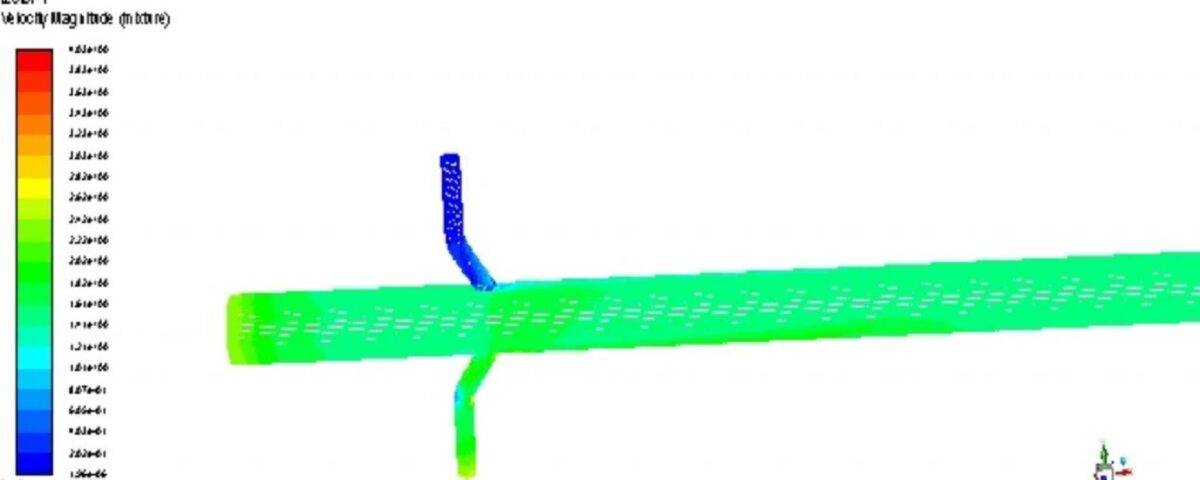
Simulation of two-phase flow and multiphase flows in Fluent are of increasing importance in the field of engineering. Two-phase flows are a subset of multi-phase flows and often include the simulation of a gas and a liquid. For example, the transformation of the liquid phase into the vapor phase in the pipe is an example of two-phase flows in the pipe. Considering that these flows are found abundantly in the industry, having expertise in simulating two-phase flows in Fluent is a requirement for many scientific and industrial activities.
The simulation of the Discrete Element Method (DEM) process in Fluent software for a two-phase mixing pipe involves several stages designed to analyze the behavior of fluid and solid particles in this system. Initially, the geometry of the mixing pipe and the physical and chemical properties of the two phases, namely the fluid and the solid particles, are defined. Then, a suitable computational mesh is created for modeling.
Next, boundary and initial conditions, including inlet velocities, temperature, and pressure, are established. The simulation examines flow behavior, particle distribution, and mixing within the pipe. Finally, the simulation results are evaluated to assess the mixing performance and optimize the design of the pipe, potentially improving industrial processes related to two-phase mixing.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the simulation of the Discrete Element Method (DEM) in Fluent software for a two-phase mixing pipe serves as a critical tool for understanding and enhancing mixing processes across various industries. This simulation provides precise insights into particle behavior and phase interactions, enabling us to optimize system performance and increase efficiency. The results obtained can identify weaknesses and improve the design of pipes and mixing processes, ultimately leading to reduced energy consumption, minimized waste, and enhanced product quality. Overall, employing this simulation technique can have a significant impact on the efficiency and success of industrial processes involving two-phase mixing.
In this project, Ansys Fluent software is used to simulate a mixing pipe using the two-phase DEM method.