Introduction
The SHAZAND Pet. Co. Complex is one of the country’s key infrastructure projects developed to meet domestic needs and promote petrochemical industry exports. This project was approved in 1984, and after design, engineering, and installation phases, its first phase began production in 1993. Subsequently, to enhance production and diversify outputs, additional units were completed, including the last unit, the ethoxylate unit, which was launched in 2003. Since 2000, efforts to expand capacities have also been approved, leading to the completion of the first phase in late 2005 and the second phase in summer 2007. After the expansion, the complex has a total production capacity of 1,469,000 tons per year.
The SHAZAND Pet. Co. Complex is one of the largest petrochemical complexes in Iran, with an annual capacity of 1,700,000 tons of base, polymer, and chemical products. It supplies 4% of ethylene, 5% of heavy polyethylene, 7% of linear low-density polyethylene, 10% of propylene, and 7% of polypropylene produced in the country.

Overview of Shazand Petrochemical Complex
1. Geographical Location and Establishment
– Located in MARKAZI Province, IRAN, 35 km northeast of ARAK, the complex has been operating since 1994 as part of IRAN’s petrochemical industry.
2. Processes and Products
– The complex includes various units producing a range of products, with key processes and products including:
– Ethylene: Essential for producing various products like polyethylene and polypropylene.
– Propylene: A key component for plastics and specialty chemicals.
– BTX Compounds (Benzene, Toluene, Xylene): Used for producing solvents, plastics, and various chemicals.
– Polymers: Including polyethylene and polypropylene for uses in packaging, construction, and automotive industries.
– C4 and C6 Derivatives: Producing compounds like dienes, silicones, and light and heavy hydrocarbons.
3. Production Capacity and Scale
– Known for its high production capacity, the complex utilizes modern technologies to produce millions of tons of petrochemical products annually.
4. Infrastructure and Equipment
– Equipped with advanced infrastructure, including:
– Innovative separation and distillation systems
– Laboratory equipment for quality control
– Adequate transportation systems for raw materials and final products.
5. Environmental and Safety Impacts
– Committed to environmental sustainability and safety by adhering to international safety and health standards to minimize adverse environmental impacts, including:
– Environmental management systems
– Waste and pollutant reduction efforts
– Ensuring worker safety and workplace health.
6. Partnerships and Collaborations
– The complex collaborates with domestic and international companies, leveraging advanced technologies to enhance production and enter international markets.
7. Challenges and Future Outlook
– Facing global market fluctuations, tariff issues, and the need for technological updates, the complex aims to be an innovative center in petrochemical industry and enhance exports.
The SHAZAND Pet. Co. Complex plays a crucial role in meeting the industrial needs of the country and exporting petrochemical products, with high potential for future development despite existing challenges.
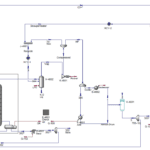
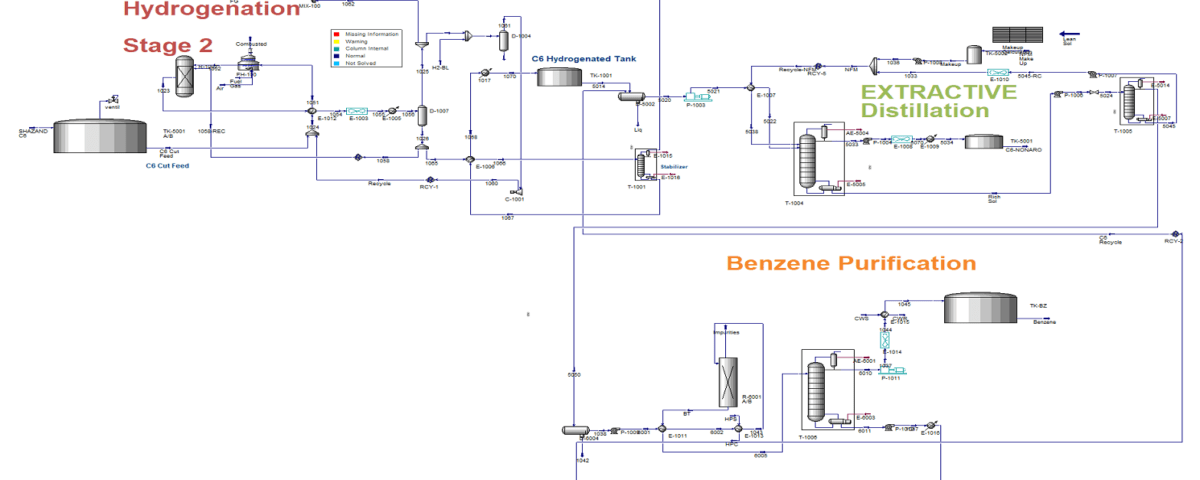
C6 Cut Separation at Shazand Petrochemical
The C6 cut separation process is a key focus in petrochemical production, requiring thorough examination and a deep understanding of various technical, economic, and environmental aspects. The following details outline C6 cut separation:

1. Definition and Importance of C6 Cut:
– Components: The C6 cut typically includes hydrocarbon compounds like hexane, 2-methylpentane, 3-methylpentane, and cyclohexane, with significant industrial applications.
– Industrial Uses: Hexane is used as a solvent in food and chemical industries, while cyclohexane is a key raw material in producing nylon and other polymers.
2. Separation Methods:
– Distillation: A traditional method based on temperature differences, requiring specific equipment and processes to separate C6 mixtures.
– Adsorption: Using adsorbent materials to separate different hydrocarbons, especially effective in high-throughput environments.
– Aspen HYSYS: A relatively new method based on isotopic exchange for hydrocarbon separation, offering higher efficiency compared to traditional methods.
3. Technical Analysis:
– Infrastructure: Assessing existing facilities in the complex to identify the need for upgrades or new equipment for the separation process.
– Equipment Performance: Evaluating the performance of existing equipment and ensuring the up-to-date technology for optimal separation.
4. Economic Analysis:
– Costs: Estimating costs related to the separation process, including investment, operational, and maintenance expenses.
– Market Products: Researching market prices for separated C6 products and analyzing the financial advantages of separation for the petrochemical complex.
5. Environmental Considerations:
– Environmental Impact: Evaluating the environmental impacts of C6 separation in line with local and international regulations, ensuring minimal adverse effects.
– Sustainability: Assessing sustainable practices and strategies to minimize waste and energy consumption during separation processes.
6. Risks and Challenges:
– Risk Identification: Evaluating financial and operational risks that may arise during the separation process.
– Risk Management Strategies: Developing plans to mitigate risks and optimize separation techniques.
C6 cut separation at the Shazand Petrochemical Complex represents a valuable project with high potential for increased revenue and product diversification. However, performing a thorough feasibility study across technical, economic, and environmental aspects is essential, with close collaboration among industry experts, suppliers, and environmental organizations to ensure project success.
Feasibility Study
In general terms, feasibility involves analyzing all factors related to a project, including economic, technical, legal, and planning considerations. The outcome of feasibility studies determines a project’s likelihood of success prior to investment, allowing managers to gather information and avoid blindly entering high-risk ventures. Essentially, feasibility assesses the practicality of a proposed plan.
Feasibility explores the viability of an idea, determining whether pursuing it is beneficial and feasible. Various stakeholders, including industrialists, farmers, and investors, can conduct feasibility studies before starting their businesses to ensure the sustainability of their idea. The sooner individuals realize an idea may not work, the more time and resources they save while exploring alternative ideas.
Process Description
Analyzing the feasibility of C6 cut separation from the Shazand Petrochemical Complex involves various considerations, including technical, economic, and environmental aspects. Key factors include:
1. Understanding C6 Cut:
– Definition and Components: The C6 cut refers to a specific hydrocarbon fraction including compounds with six carbon atoms, such as hexane and cyclohexane. Hexane is commonly used as a solvent, while cyclohexane is vital for nylon production.
– Industrial Applications: The C6 cut can be used in producing solvents, chemicals, and fuels, and understanding these applications aids economic assessments of separation.
2. Technical Feasibility:
– Separation Techniques: Identify suitable separation methods (distillation, adsorption, or membrane technologies) that could enhance separation efficiency and reduce costs.
– Equipment Requirements: Check if existing facilities can support the separation process or if new equipment is necessary (e.g., storage tanks, distillation columns, pumps, control systems).
– Process Integration: Analyze how C6 cut separation fits within overall production plans at the Shazand Petrochemical Complex, assessing potential efficiencies and operational cost reductions.
3. Economic Feasibility:
– Market Demand: Investigate the market for products derived from the C6 cut to help determine the project’s profitability and potential commercial viability.
– Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis that accounts for initial investments, operational costs, and projected revenues from sales of separated products, highlighting competitive advantages.
– Investment and Returns: Evaluate the necessary investments for separation and estimate the return on investment (ROI), assessing financial resources and risk factors.

4. Aspen HYSYS Technology:
– Application of Aspen HYSYS: A modern separation method based on isotopic exchange can significantly improve separation yields.
– Benefits: Aspen HYSYS offers specific advantages, including high accuracy in separating isomers and reduced energy consumption compared to traditional distillation methods.
5. Environmental Considerations:
– Emission Impacts: Assess environmental impacts of the separation process to ensure compliance with local and international greenhouse gas and waste management regulations.
– Sustainability: Implement sustainable practices to minimize waste and energy consumption, utilizing green technologies and optimizing resource use.
6. Regulatory and Compliance Aspects:
– Review legal frameworks governing petrochemical production and waste management in the jurisdiction, ensuring that the separation process adheres to health and safety regulations, including necessary permits and environmental certifications.
7. Risk Evaluation:
– Identify potential financial, operational, and environmental hazards associated with the separation process. Developing risk reduction strategies and planning for unforeseen consequences can enhance the reliability and success of the project.
Conclusion
A comprehensive feasibility study that thoroughly analyzes these aspects can evaluate the practicality of C6 cut separation in the Shazand Petrochemical Complex using Aspen HYSYS technology. This research should involve collaboration with separation technology experts and financial managers to provide a clear picture of the project’s commercial and technical potential.
Analysis and Feasibility of C6 Cut Separation at Shazand Petrochemical
In this project, the analysis and feasibility of C6 cut separation at Shazand Petrochemical has been simulated using Aspen HYSYS version 14.