Introduction
In today’s industrial world, cooling towers are recognized as vital components in production and air conditioning processes. These systems play a crucial role in maintaining temperature and equipment efficiency, significantly impacting the operational costs and energy consumption of an industrial unit. The economic analysis of cooling towers involves a thorough evaluation of their costs and benefits, energy performance, and identification of factors affecting the efficiency of these systems. This analysis enables companies to make better investment decisions and optimize processes, leading to substantial improvements in productivity and overall cost reduction.
Cooling towers are essential equipment in industrial and power plant systems, crucial for temperature control and process efficiency. The economic analysis of cooling towers includes examining their costs, benefits, lifespan, maintenance expenses, and energy consumption. Optimal selection of the type and capacity of a cooling tower can significantly affect the operational costs of an industrial unit. Additionally, considering climate change and increasing sensitivity to environmental issues, the economic analysis should encompass energy efficiency evaluations and environmental impact reduction measures. Ultimately, these analyses assist managers in making informed decisions regarding investments and optimizing the performance of their thermal systems.
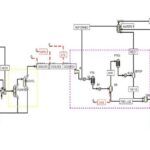
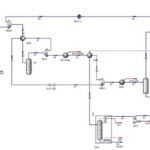
For instance, the following figure from the related article analyzes the treatment of cooling tower discharge water (CTBD) in coal power plants using reverse osmosis (RO) and direct contact membrane distillation (DCMD). The results indicated that DCMD, utilizing waste heat, performs better in water savings and costs compared to RO, with a treatment cost of 3.38 Ұ/m3. Furthermore, DCMD is more economically viable when electricity prices exceed 0.31 Ұ/m3.

Process Description
The cooling tower operation process is fundamentally based on water evaporation as a heat transfer system. In this process, hot water from industrial sources or air conditioning systems is pumped into the cooling tower. The water is then dispersed through nozzles as fine droplets over the packing surfaces inside the tower, increasing the contact area between the water and the surrounding air. Cold, dry air flows upward from the bottom of the tower, coming into contact with the water droplets, allowing a portion of the water to evaporate. This evaporation absorbs the latent heat of the water, reducing the temperature of the remaining water. The cooled water is then returned to the system for reuse as a cooling source. This continuous cycle not only helps in reducing energy consumption but also enhances the overall efficiency of thermal systems.
The economic analysis of cooling towers includes a detailed examination of costs and savings associated with their operation. Initially, upfront costs, including purchase, installation, and commissioning expenses, should be considered. Subsequently, ongoing costs such as electricity consumption, water costs, and periodic maintenance are analyzed. Reducing energy consumption through appropriate cooling tower selection and process optimization, especially in energy-intensive industries, can lead to significant savings. Additionally, the useful life of the tower and potential repair and replacement costs are considered to provide managers with a comprehensive view of initial investment and return on investment. Moreover, assessing environmental impacts and compliance with protective standards can influence costs and public brand perception. Ultimately, this analysis aids decision-makers in choosing the most optimal and cost-effective options for investing in and maintaining cooling towers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the economic analysis of cooling towers serves as a key tool in managing costs and optimizing the performance of industrial and power generation systems. Given the significant effects of these systems on energy efficiency and ongoing costs, investors and managers can make better decisions regarding the type and design of cooling towers by accurately assessing costs, benefits, and environmental impacts. These analyses not only contribute to cost reduction and productivity enhancement but also play a vital role in meeting environmental standards and preserving natural resources. Therefore, paying attention to the economic and environmental aspects in the design and operation of cooling towers is essential, especially in today’s world in search of sustainable solutions.