Introduction
All engineering projects contain documents that are considered the main project documents. Engineers from various fields, including chemical, mechanical, instrumentation, metallurgy, etc., need to be familiar with these documents to effectively perform their roles in the project. These documents exist from the beginning to the end of each project and even afterward. Two important diagrams in the petrochemical industry that are encountered by nearly all disciplines, from chemical and process engineers to civil engineers, are the PFD (Process Flow Diagram) and P&ID (Piping and Instrumentation Diagram).
Familiarity with these documents and skills in working with them is a significant advantage for job market competitiveness. It is not necessary to work in a petrochemical plant or refinery; even if you are employed as an engineer at a process equipment manufacturing company, such as pumps, compressors, turbines, and heat exchangers, it is crucial to be acquainted with P&ID diagrams to submit to employers.
Process Description
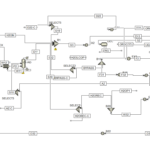
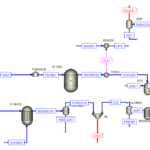
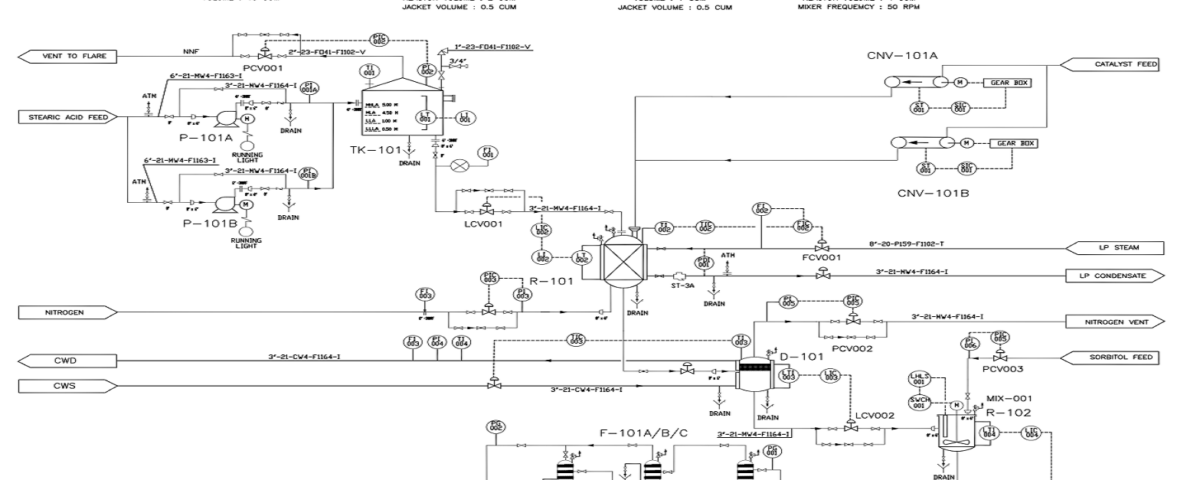
The diagram provided offers an overview of the sorbitan production process graphically. Such diagrams are used as part of the technical documentation for a factory or industrial unit, providing precise information about material flows, equipment, and operations in various units.
– Preparation of Raw Materials: The raw materials, including stearic acid, sorbitol, and catalyst, are mixed in the tank TK-101.
– Initial Reaction: The mixture is pumped to the primary reactor (R-101), where the initial chemical reaction occurs under specific temperature and pressure conditions.
– Separation: The product output from the primary reactor enters the vapor-liquid separator (D-101), where vapor is separated from the liquid and directed to the heat recovery system.
– Secondary Reaction: The separated liquid from the previous stage is transferred to the secondary reactor (R-102) for the second chemical reaction, completing the sorbitan production process.
– Separation and Purification: The final sorbitan product is separated from the reaction mixture in the filter (F-101) and purified.
– Process Control: Control valves (CNV-101) are used to regulate the flow and pressure of fluids in the system. Pumps (P-101) are also utilized for transferring materials between different units.

Conclusion
– Importance of Safety: In chemical processes, adhering to safety protocols, including the use of personal protective equipment, fire extinguishing systems, and proper ventilation, is of utmost importance.
– Quality Control: Regular sampling of raw materials, intermediate products, and final products is essential to ensure product quality is maintained.
– Energy Consumption Optimization: Utilizing heat recovery systems and precise control of process parameters can help reduce energy consumption.
– Environmental Protection: Proper wastewater management and reducing pollutant emissions into the environment are critical considerations.
Design of Technical Knowledge Maps for Sorbitan Production
In this project, the design of technical knowledge maps for sorbitan production has been carried out.