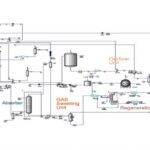
Introduction
The design of engineering documents and diagrams related to the Ethylene Glycol Purification Unit holds significant importance in industrial processes, as these documents lay the foundation for the optimal structure and performance of systems. Block Flow Diagrams (BFD) provide a simple and overall view of the process, depicting the main production stages, whereas Process Flow Diagrams (PFD) offer more detailed information on material flows and operational conditions. Concurrently, Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (PID) accurately illustrate the technical aspects and connections of equipment, including control and measurement systems. Furthermore, Utility Flow Diagrams (UFD) address the energy needs and essential resources for optimal performance.
These documents not only serve as communication tools among engineers, designers, and execution teams, but also facilitate the analysis and optimization processes. Proper design of these diagrams can aid in identifying deficiencies and potential hazards at various stages of the process, paving the way for performance optimization and cost reduction. Additionally, utilizing advanced software for designing these documents enhances accuracy and efficiency, while enabling the simulation of various operational conditions. Ultimately, these documents serve as the basis for the documentation required for the startup, operation, and maintenance of the Ethylene Glycol Purification Unit, ensuring the optimal and safe performance of the system throughout its lifecycle.
Preliminary Design Documents
This section in an ethylene glycol purification project includes documentation meant to provide an overview of the process and establish the preliminary requirements of the unit. At this stage, various processes, such as hydrolysis, distillation, and separation, are examined to ensure optimal unit performance. The project’s goals and needs are also outlined in these documents, which may include economic objectives such as cost reduction, increased purity levels, and improved quality of the final product.
Additionally, practical requirements such as compliance with environmental and safety standards are included in this section. Ultimately, the preliminary specifications of the unit in the preliminary design documents include determining production capacity, equipment dimensions, and the type and specifications of machinery and system components. Generally, the preliminary design documents play a vital role in establishing a solid foundation for the subsequent design and implementation stages.
BFD (Block Flow Diagram)
The Block Flow Diagram (BFD) provides a simple overall view of the process. In this diagram, the main stages of the Ethylene Glycol Purification Unit are represented as separate blocks. Each block represents a step in the process, such as production, cooling, separation, etc., which deals with the exchange and flow of materials among these stages. BFDs allow designers and engineers to gain a comprehensive perspective of the entire process and easily identify the quality and relationships between different stages.
PFD (Process Flow Diagram)
The Process Flow Diagram (PFD) provides more detailed information on material flows, energy, and operational conditions compared to BFD. Each stage of the ethylene glycol purification process is displayed along with technical specifications, flow rates, temperatures, pressures, and other critical parameters. PFDs typically include specific symbols for equipment, piping, and points of material input and output, clearly indicating how materials move and interact in the process.
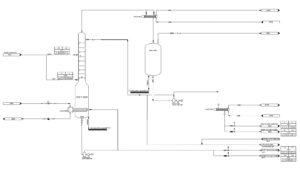
PID (Piping and Instrumentation Diagram)
The Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (PID) is one of the essential tools in designing and documenting industrial units. This diagram provides complete information about equipment, piping connections, and control instruments, clearly showing how each pipe and device is interconnected. Additionally, PID includes details regarding sensors, valves, control equipment, and measurement points, and can incorporate performance specifications such as the type and technical characteristics of the sensors, valves, and other equipment used in the system. The design of the PID is organized so that all components and mechanisms necessary for an industrial process are clearly and systematically presented, allowing all stakeholders, from designers to operators and technicians, to easily understand operational needs.
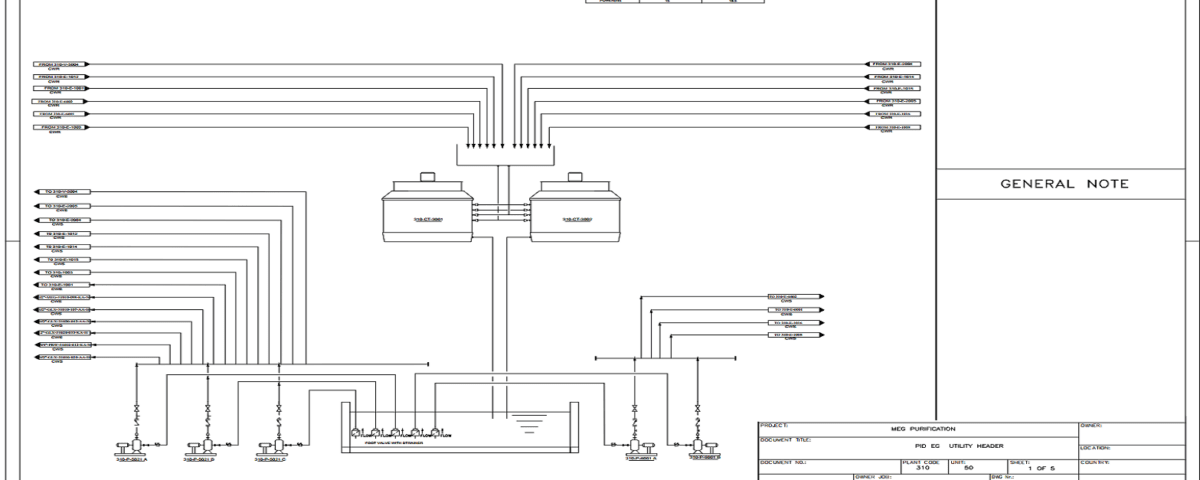
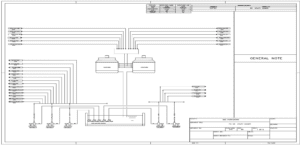
UFD (Utilities Flow Diagram)
The Utilities Flow Diagram (UFD) focuses on including and reviewing the energy needs and essential resources for optimal process performance. This diagram includes information about water, steam, electricity, and other energy sources such as natural gas and compressed air, along with a clear depiction of how these utilities are supplied to different stages of the process. UFDs help engineers and managers optimize existing systems and achieve good records of efficiency and resource consumption by analyzing utility flows. These diagrams clearly show how various energy resources are delivered to different equipment and processes, and they also identify the interactions between different resources, helping estimate operational costs.
Required Technical Knowledge
To effectively design key documents such as BFD, PFD, PID, and UFD, a deep and comprehensive understanding of several specialized fields is essential. Chemical engineering serves as a fundamental basis, requiring mastery of chemical processes and reactions so that designers can accurately identify and analyze production stages and process variations. This knowledge enables the prediction of various materials’ behaviors under different operational conditions. Along with this, engineering design is also highly important; proficiency in design software such as AutoCAD and Aspen Plus not only assists in creating accurate and clear representations of equipment and connections but also provides the ability to simulate processes to predict and optimize their performance.
Additionally, process control is another critical aspect that includes knowledge of system control and automation. Understanding these concepts allows designers to create effective control systems for monitoring and managing processes. Finally, familiarity with instrumentation and sensor systems, along with knowledge of control mechanisms, provides designers with the awareness needed to integrate measurement and control elements properly within the overall system of a process. By combining this knowledge, specialists will be able to design strong and effective documents that contribute not only to optimizing unit performance but also to ensuring safety and operational efficiency.
Safety and Hazard Analysis (HAZOP)
Safety and Hazard Analysis (HAZOP) is one of the key stages in the design and implementation of industrial projects, including the Ethylene Glycol Purification Unit, which identifies hazards and assesses process safety while ensuring that safety needs are met. In this stage, the identification of potential hazards begins, obtained through a thorough examination of processes, equipment, and operational conditions. This identification includes analyzing scenarios where hazards such as chemical leaks, equipment failures, or abnormal operational conditions may occur.
After identifying these hazards, a vulnerability analysis is conducted to identify system deficiencies and vulnerabilities. Weaknesses may include the lack of certain safety measures, improper equipment design, or insufficient training of personnel. Ultimately, risk management is carried out by developing control and preventive strategies to reduce the likelihood of hazards and their consequences. These strategies may include design modifications, installing additional safety systems, or training programs for staff. Overall, HAZOP not only helps in identifying and analyzing hazards but also serves as an essential factor in ensuring the safety and productivity of industrial operations.
Modeling and Simulation of Processes
Modeling and process simulation are vital tools in the design and optimization of Ethylene Glycol Purification Units, allowing engineers to study system behavior under various conditions. In this process, software tools such as Aspen Plus, HYSYS, and ChemCAD are used. These software programs provide powerful means to simulate the behavior of individual operational units and their interactions at the system level. By utilizing these software programs, engineers can alter various conditions such as temperature, pressure, and feed composition to examine their effects on outputs and overall system performance.
Simulation results and analyses typically include evaluations of key components such as conversion efficiency, the quality of the final product, and energy consumption. These analyses help identify the most optimal operational conditions and highlight potential improvements in design or processes. Ultimately, modeling and simulation serve as effective tools in reducing execution risks, optimizing costs, and achieving better performance in industrial units.
Planning and Scheduling
Planning and scheduling in a project are critical aspects of managing any industrial project, including Ethylene Glycol Purification Units. The project phases and their execution timelines typically involve several key stages, starting from pre-engineering and design to equipment installation and then testing and startup. For each of these stages, specific timelines are set to help balance available resources with project goals.
Additionally, resource and personnel allocation is another key factor in project success. At this stage, human and financial resources must be effectively allocated to meet various project needs. Engineers, technicians, and other team members are purposefully assigned to each project phase according to their experience and expertise. Furthermore, financial resources are managed precisely to prevent any deficits or cost overruns. This allocation also includes securing the necessary raw materials and equipment for the project’s execution phases. Overall, careful planning and scheduling, along with optimal resource allocation, can lead to reduced costs, expedited execution, and enhanced project quality.
Technical Specifications of Equipment
The technical specifications of equipment are a vital part of any industrial project, especially in Ethylene Glycol Purification Units, and include detailed information about the type and efficiency of equipment along with installation and startup instructions. The type and specifications of key equipment usually cover main process units such as distillation columns, heat exchangers, and storage tanks, each playing a significant role in the overall system performance. Additionally, adequately designed and highly efficient heat exchangers effectively transfer the required heat and contribute to optimizing energy consumption in the process.
Regarding installation and startup instructions, this section includes step-by-step procedures for installing, calibrating, and commissioning equipment. These instructions are meticulously prepared with references to safety considerations and operational prerequisites to avoid problems during installation and in the future. They encompass aspects such as assessing environmental conditions, correctly connecting electrical and hydraulic systems, and conducting performance tests before final commissioning. Furthermore, necessary training for personnel regarding the installation and maintenance of equipment is also addressed in this section. Ultimately, adhering to these technical specifications and related instructions enhances equipment efficiency, reduces maintenance costs, and ensures workplace safety and health.
Economic Analysis
Economic analysis is a key stage in evaluating industrial projects, particularly in Ethylene Glycol purification projects, providing engineers and managers with the opportunity to accurately assess the financial aspects of a project. Cost estimation and profitability include analyzing all direct and indirect costs of the process, including initial capital investment, operating costs, and expenses related to human resources and maintenance. By considering these costs and calculating projected revenues from the sale of the final product, profitability estimates of the project can be made.
Additionally, sensitivity analysis investigates how changes in key parameters affect the project’s financial outcomes. Specifically, this analysis examines how fluctuations in raw material costs, sale prices, and other variables can impact profitability and overall costs. By simulating various scenarios, it is possible to determine which factors correlate most significantly with financial performance and how related risks can be managed. Overall, economic analysis, by combining cost estimates, profitability evaluations, and sensitivity analysis, contributes to more informed decision-making regarding project execution and resource allocation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the design and documentation of key documents such as BFD, PFD, PID, and UFD hold paramount importance in industrial processes, particularly in Ethylene Glycol Purification Units. These documents not only assist engineers and technicians in clearly understanding processes and identifying interactions between different equipment but also guarantee compliance with safety and operational standards. By providing detailed information about material flows, energy, and operational conditions, these documents lay the groundwork for optimizing performance, reducing costs, and conserving resources. Moreover, facilitating equipment installation and maintenance, as well as identifying weaknesses and possible optimizations, are other key benefits of these documents. Ultimately, effectively utilizing these tools enhances productivity, reduces safety risks, and improves product quality, contributing to the flourishing and sustainability of the chemical industry in the future.
To enhance performance and productivity in the design, establishment, production of technical knowledge and engineering innovations, and optimization of Ethylene Glycol production and purification units in Saudi Arabia, Anil Pars Company has undertaken comprehensive simulation and optimization studies on the key processes of this unit. These studies include:
1. Feasibility study of an Ethylene Glycol purification and separation unit with a capacity of 15 KTY.
2. Production of basic engineering documentation; Operation Manual for the Ethylene Glycol Unit.
3. Performance analysis of production and resource management at the Arta Chemical Plant: Assessment of performance reports, human resources, and raw materials.
4. Design of the capacity plan and technical knowledge for the production plant of MEG, DEG, and TEG with a capacity of 15 KTY.
5. Design of documents, technical knowledge, and diagrams for BFD, PFD, PID, and UFD of the Ethylene Glycol Purification Unit.
6. Project management, control, and endorsement of the engineering documents for the MEG, DEG, TEG production unit.
7. Simulation and optimization of the Monethylene Glycol (MEG) purification process with a production capacity of 10 KTY.
8. Simulation and optimization of the Monethylene Glycol (MEG) purification process with a production capacity of 15 KTY.
These actions aim to increase the production of technical knowledge and innovative engineering, reduce production costs, optimize Ethylene Glycol production processes, and develop up-to-date units. The ultimate goal is to ensure better product quality and enhance the company’s competitiveness in the market.
Design of Documents, Technical Knowledge, and Diagrams for BFD, PFD, PID, UFD of the Ethylene Glycol Purification Unit
In this project, the design of documents, technical knowledge, and diagrams of BFD, PFD, PID, and UFD for the Ethylene Glycol Purification Unit has been completed.