Introduction
In this project, a 2D model is developed for the simultaneous separation of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide from natural gas using the solvent monoethanolamine (MEA) in a hollow fiber membrane contactor. Axial and radial diffusion within the shell, shell section, and membrane are considered. It should be noted that the main source of modeling is based on the following article:
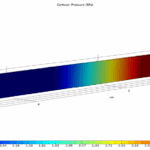
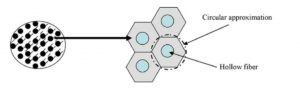
The membrane contactor consists of three parts: shell, membrane, and shell. A gas mixture (H2S, CH4, and CO2) flows inside the shell, while the solvent flows in the opposite direction inside the shell. The steady-state two-dimensional mass conservation equation is written for all three parts. The gas mixture enters the shell section (at z = L), while the solvent enters the shell section (at z = 0).
Carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide are separated due to diffusion into the membrane and subsequent absorption and reaction with the solvent. The model is developed for a section of hollow fiber, as shown in the figure above, where the solvent has a fully developed parabolic velocity profile and The fibers are surrounded by a laminar gas flow in the direction opposite to the liquid flow. The figure below shows the cross-section of the membrane contactor.
In this project, modeling and optimization of CO2 and H2S absorption using amine in COMSOL software has been performed. Modeling has been carried out in three states: dry membrane, semi-wet membrane, and wet membrane. The following images show a portion of the simulation results.This project has a report.
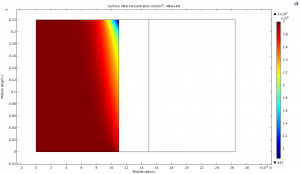
Concentration Profiles of MEA, MEA+, MEACOO-, and HS- Along the Membrane Length
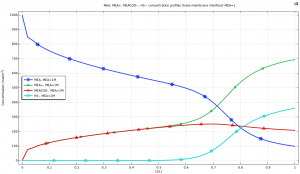
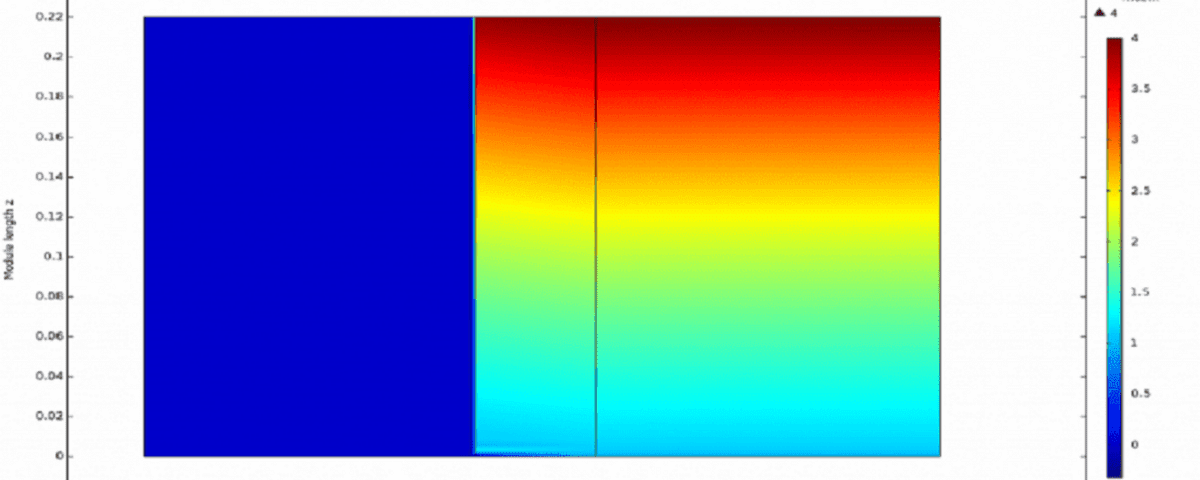
Semi-wet Section
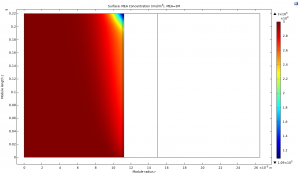
1. CO2 Absorption on Semi-Moist Membrane
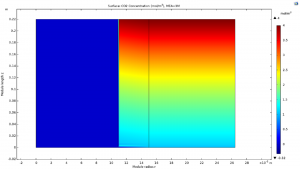
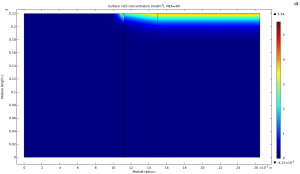
2. Adsorption of H2S on Semi-Moist Membrane
3. MEA Profile in Semi-Moist Membrane
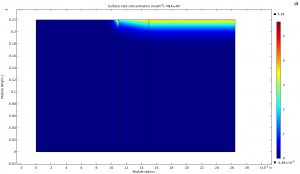
Wet Section
1. CO2 Absorption on Wet Membrane
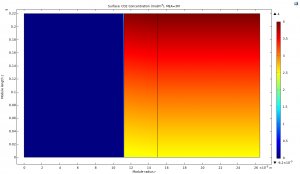
2. Adsorption of H2S on Wet Membrane
3. MEA Profile in Wet Membrane