Drying Oil
A drying oil is a type of oil that, when exposed to air, oxidizes and polymerizes to form a solid, tough film. This process occurs through chemical reactions that create cross-links between the oil’s molecules. Drying oils are a key component in oil-based paints and varnishes. Common examples of drying oils include linseed oil, tung oil, poppyseed oil, perilla oil, and walnut oil. Oils are also primary ingredients in the production of alkyd resins.
Difference Between Drying and Non-Drying Oil
Drying Oils: These oils have the property of hardening and drying when exposed to air over time. This process is due to chemical reactions within the oil that create cross-links between oil molecules. Drying oils are widely used in paints, resins, and protective coatings.
Non-drying Oils: Unlike drying oils, these oils do not dry when exposed to air and require heat or solvents to cure. They are often used in cosmetics, skincare products, and certain foods.
Popular Drying Oils
- Flaxseed oil
- Stand oil (a thickened version of flaxseed oil)
- Tung oil
- Poppyseed oil
- Perilla oil
- Walnut oil
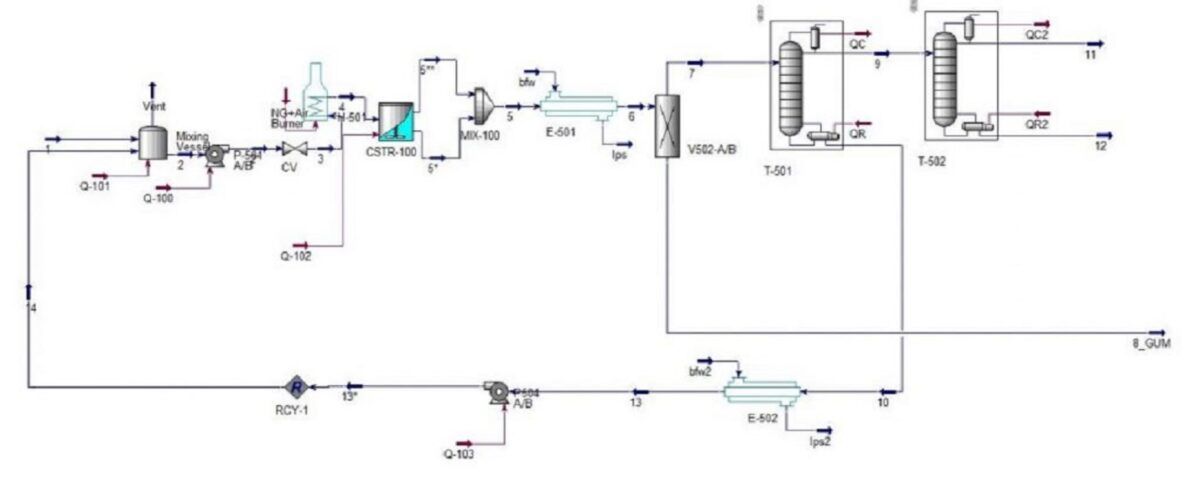
Feasibility Study of Oil Drying with Aspen hysys
This comprehensive project includes detailed economic calculations, equipment pricing, profit margins, and TCI (Total Capital Investment) tables for a drying oil production plant. The project is complete with an Aspen Hysys simulation file, a presentation deck, and an instructional video. The accompanying 30-page Word document provides a thorough explanation of the project.