Introduction
Pigging is a process involving the insertion of a specialized tool, called a pig, into a pipeline to accomplish various objectives such as cleaning, inspection, or separating different fluids. This process is widely used in the oil, gas, petrochemical, and many other industries for the maintenance and optimal operation of pipelines.
Objectives of Pigging
- Pipeline cleaning: Removal of deposits, rust, wax, water, and other contaminants that accumulate inside pipelines over time.
- Pipeline inspection: Detection of internal defects and anomalies such as corrosion, cracks, deformation, and wall thinning.
- Fluid separation: Separation of different fluids like oil and gas or water and oil in multiphase pipelines.
- Internal pipeline coating: Application of protective coatings on the inner walls of pipelines to prevent corrosion and extend their lifespan.
- Pipeline drying: Removal of moisture from inside pipelines before repairs or restarting operations.
Pigging Process
- Preparation: Before pigging, the pipeline must be completely drained and cleaned. The appropriate pig is selected and prepared based on the operation’s objectives.
- Pig introduction: The pig is introduced into the pipeline using fluid or gas pressure.
- Pig travel: The pig travels through the pipeline at a specified speed, performing the intended operation.
- Pig removal: After the operation is complete, the pig is removed from the end of the pipeline.
- Inspection and data analysis: Data collected by inspection pigs is analyzed to assess the pipeline’s condition.
Benefits of Pigging
- Reduced maintenance costs: Early detection of defects prevents major problems and costly repairs.
- Increased pipeline lifespan: Cleaning and coating the inner walls of pipelines extend their lifespan.
- Improved pipeline efficiency: Removal of deposits and contaminants increases pipeline capacity.
- Reduced environmental risks: Prevention of leaks and contamination reduces environmental hazards.
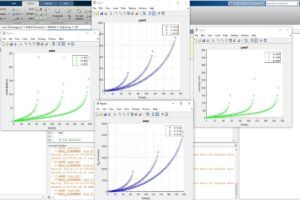
In this project, the flare process, which is one of the main units of supplying gas to refineries, has been modeled with the help of MATLAB software. It is assumed that this process takes place in a completely horizontal pipe. And it has been done for 2 different fluids with different viscosity and properties (water and diesel). The written code, which is about 75 lines, has a complete report on how to parameterize and model and equations.
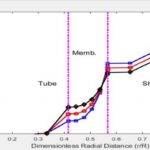
The schematic of the process is shown below: