Introduction
Acid gas removal is one of the most important stages in gas refining after extraction from underground. Carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide are the most important sour gases that are separated due to environmental concerns and to ensure the health of consumers. Therefore, the separation of sour gases is essential to prevent corrosion of gas pipelines and environmental damage. Wet wall columns are industrial equipment used to absorb sour gases from extracted methane.
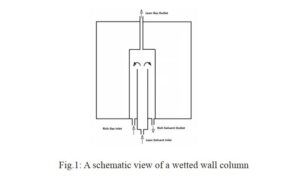
Wetted-Wall Column Operation
A wetted-wall column is a vertical device in which a thin film of absorbent solution (e.g., ammonia) flows down the inner wall. CO₂-containing gas flows concurrently with the absorbent, entering from the bottom of the column. Upon contact, CO₂ transfers from the gas phase to the liquid phase and is absorbed by the ammonia solution.
Primary Process Stages
- Gas-Liquid Contact: CO₂-laden gas enters from the bottom and comes into contact with the ammonia film on the wall.
- Mass Transfer: CO₂ transfers from the gas phase to the liquid phase, dissolving in the ammonia solution.
- Chemical Reaction: CO₂ reacts with ammonia to form ammonium carbonate and bicarbonate.
- CO₂ Separation: The CO₂-rich solution exits from the bottom and is sent to a regeneration unit to recover ammonia.
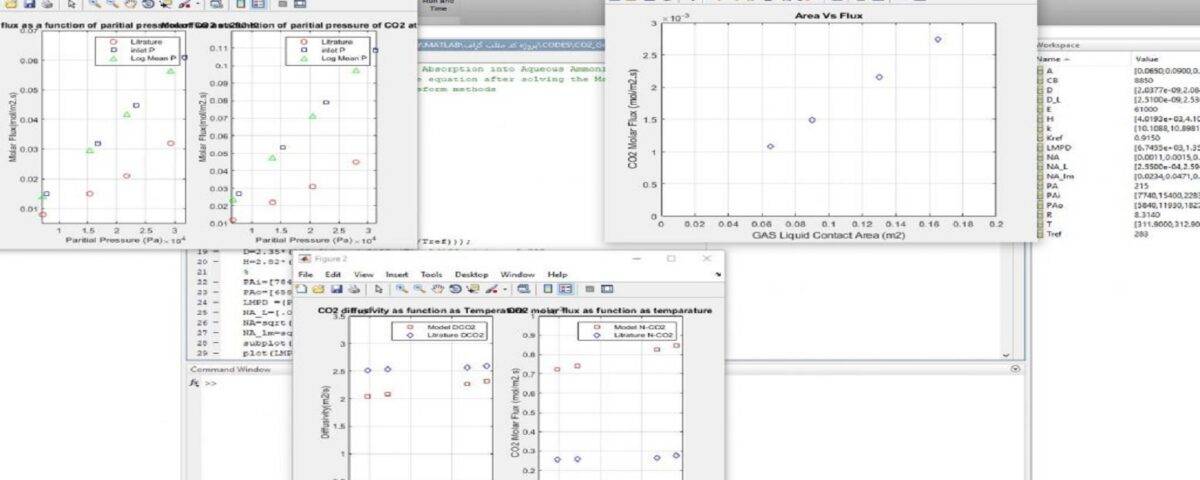
In this project, a wet wall column using monoethanolamine solution to absorb carbon dioxide gas was simulated using MATLAB software. The results were satisfactory and as expected. In this simulation, the most important part of the work was choosing a suitable method for discretizing the conservation equations and obtaining the pressure and velocity profiles.

115 lines of coding were done in MATLAB and the data of the results are in complete agreement with the article. Also, this project has a partial work report. The schematic of the model done in MATLAB is shown in the figure below.