Introduction
Ethyl acetate (ethyl ethanoate, acetic acid ethyl ester, or ethyl acetic acid) is a neutral, colorless liquid with a fruity, pleasant, and mild odor. Ethyl acetate is miscible with most common organic solvents in all proportions. Its solubility in water at 20°C is a maximum of 7.7% by weight, while it absorbs 3.3% of water at the same temperature. The azeotrope formed with water boils at 70.4°C and contains 8.5% water by weight.
Applications of Ethyl Acetate
Ethyl acetate is considered one of the best low-boiling point solvents due to its excellent solvent power and favorable evaporation rate. It is used as a primary solvent in the production of nitrocellulose and cellulose acetate lacquers, adhesives, and coatings suitable for artificial leather. It is used in the preparation of organic materials (esters and pharmaceuticals) and as an extraction agent (extracting water from food in a vacuum) and cleaning agent (paint solvent).
In addition, ethyl acetate is used as a gelling agent in the production of gunpowder, as a flavor and fragrance in the perfume industry, as a denaturant, as an aid in the production of carbonless paper and post-it notes, and as a component of polishes. Ethyl acetate is also used as a solvent for the isocyanate component of polyurethane coatings.
Liquid-Liquid Extraction
Separation operations in which two immiscible phases are contacted are called liquid-liquid extraction operations. Typically, after the extraction operation, another separation operation such as gas absorption or distillation follows. The basis of separation in liquid-liquid extraction is the difference in chemical properties. When separation by distillation is ineffective or difficult, the extraction method from a liquid, which is one of the main alternatives, is used. Mixtures composed of components with close boiling points or substances that cannot withstand distillation temperatures even under vacuum are often separated from impurities by extraction.
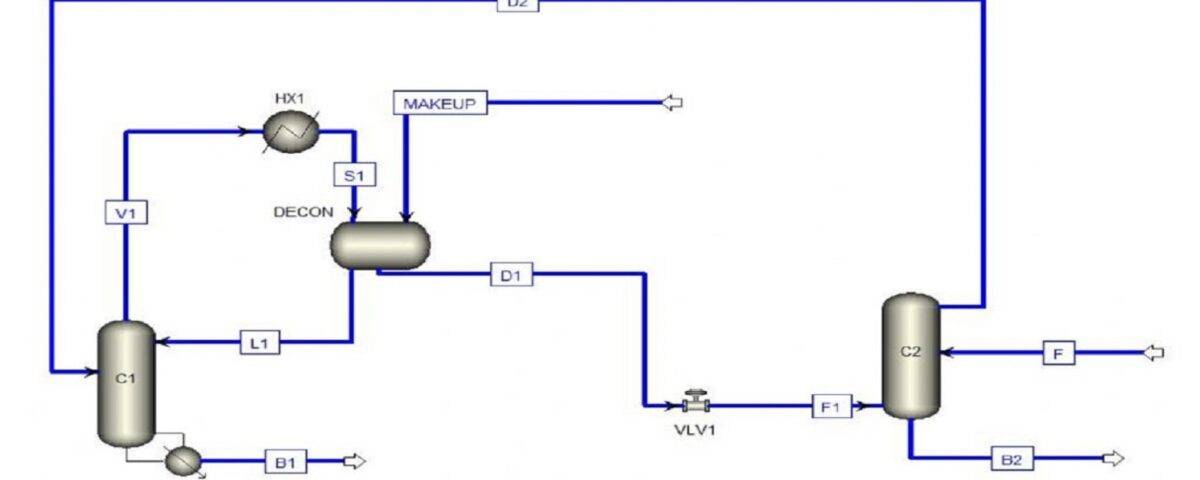
Simulation of Water and Ethyl Acetate Separation Process
In this project, the separation of ethyl acetate from water using 2-propanol as a solvent in a liquid-liquid extraction column has been simulated with Aspen Plus software.