Introduction
Heat Exchanger Network (HEN) design is a crucial aspect of chemical process design. It typically enables energy savings of 20-30% and reduces initial capital costs. This involves arranging process heat exchangers and utilities to heat or cool streams from specific sources to a specified device at the required temperature. The goal is to minimize overall costs, including process and capital costs, which are generally summarized in annual costs.
Process Description of Unit 107 in a Gas Refinery
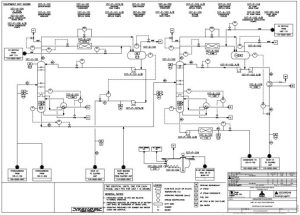
Unit 107 is designed to produce propane, butane, and C5+ hydrocarbons. The feedstock, primarily C3+ hydrocarbons, originates from Unit 105 at a pressure of 21.8 barg and a temperature of 93°C. The resulting products are then sent to various downstream units: propane to Unit 114, butane to Unit 115, and C5+ to Units 103 and 110.
This unit employs a two-column distillation process to separate liquid propane, butane, and C5+ hydrocarbons. The separated C5+ is mixed with gas condensate from Unit 103, while the sweetened propane and butane are sent to further processing or storage.
The unit’s core components are the propane column and the butane column and The propane column separates propane from the feedstock under specific temperature and pressure conditions, sending the separated propane to Unit 113 , Heavier hydrocarbons, primarily C4+ components, are extracted from the bottom of the de-butanizer column and routed to Unit 103.
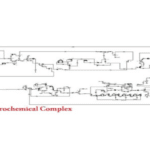
Unit 107 is an essential part of any gas refinery, as the separated condensates serve as crucial feedstock for petrochemical industries. The following figure provides a visual representation of this industrial unit, as implemented in Phases 4 and 5 of the ASSALUYEH Gas Field.
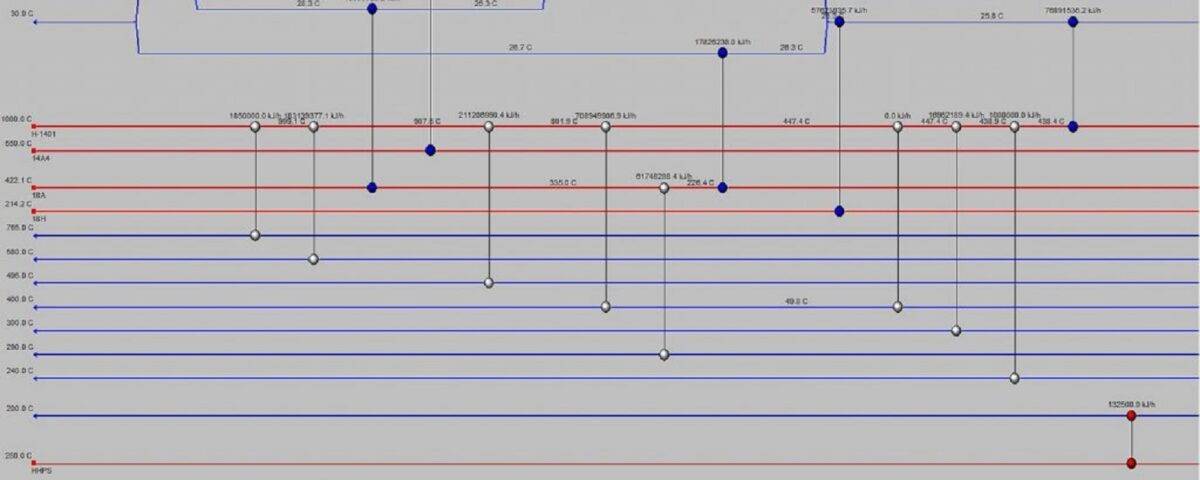
Heat Exchanger Network Analysis
As comprehensively detailed in the preceding sections, it is evident that the process involves six heat exchangers, including shell-and-tube heat exchangers, reboilers, and air coolers. The accompanying figure provides a visual representation of the heat exchangers employed in Unit 107.
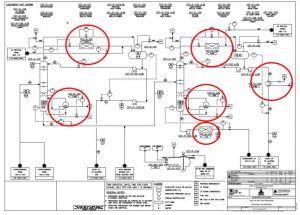
Design and Optimization of Heat Exchanger Network in the Gas Condensate Separation Unit of South Pars
The primary objective of this project is to analyze the heat exchanger network utilized in this unit and to minimize the overall energy consumption. Simulations and analyses have been conducted using Aspen Energy Analyzer software. Initially, the heat exchanger network was modeled in its conventional state using the industrial data provided in the project’s appendix(energy and material balance tables).Subsequently, the energy consumption was measured and compared after introducing modifications and designing new heat exchangers.