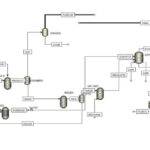
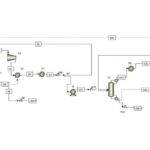
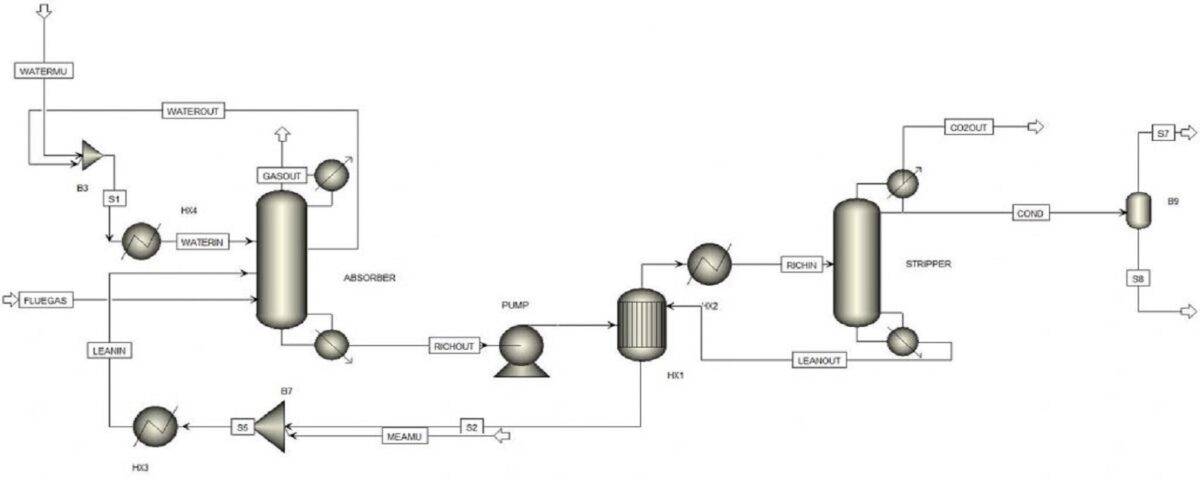
Introduction
Most CO2 separation processes rely on physical or chemical absorption of this substance in a suitable solvent. In physical absorption, the efficiency of the process is highly dependent on the amount of CO2 in the gas entering the process. As the amount of CO2 decreases, the absorption rate also decreases. This method cannot be effectively used to separate CO2 from air. Therefore, the use of chemical absorption of CO2 from air using amine solutions has shown higher efficiency and better performance.
This project simulates the absorption process using amine solutions, which are employed for the chemical absorption of CO2. Moreover, various promoters in which amine solutions separate CO2 from air in different absorption towers are investigated, and their impact on this process is observed. This project focuses on the removal of carbon dioxide from air and also analyzes the effect of ionic materials on the absorption of carbon dioxide by amines using simulation.

Traditional amine-based processes for carbon dioxide removal are evolving.By incorporating a novel ionic compound into the solvent, we have developed a modified process that significantly enhances carbon dioxide capture efficiency. This innovative approach leverages the synergistic effects of the amine and ionic compound to optimize CO2 removal.
The new process with ionic material is designed as follows:
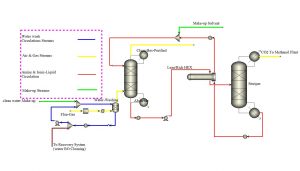
This project involves the simulation of carbon dioxide capture from air using novel solvents with Aspen Plus software.The project includes a comprehensive report and an instructional video.