Description
In addition to improving the existing processes for energy production and consumption, the increase in global demand for natural gas also requires pollution control. One of the most serious problems faced by technologies related to natural gas processes is the presence of large amounts of acid gases, which make up about 40% of output gases from wells. About 13.46% of natural gas reservoirs in the world contain more than 10% H2S and about 26.9% of these reservoirs contain more than 10% CO2 gas. In this project, we will simulate the removal of carbon dioxide from natural gas with the help of MEA.
Several methods have been proposed to reduce the amount of acid gases in natural gas, among which chemical adsorption, physical adsorption, hybrid process, surface adsorption using a solid column and using a membrane can be mentioned. Among these methods, the adsorption of acid gases by a liquid solvent (chemical adsorption) is the most common method used in the gas sweetening industry.

Sweetening of Natural Gas
In the 1930s, alkanol amines were used for gas sweetening for the first time. And from that time until the 1970s, Mono Ethanol Amine (MEA) was the most used. but since the 1970s, due to the disadvantages of Mono Ethanol Amine, such as corrosion and solvent wastage, Di Ethanol Amine (DEA) replaced this amine. Since the mid-1970s and especially in the last two decades, methyl diethanolamine (MDEA) has been widely used in the gas industry for solvent recovery due to its advantages. Among these advantages, we can mention the ability to selectively separate hydrogen sulfide in the presence of carbon dioxide, high stability and low energy consumption.
Alkanol amines generally consist of at least one hydroxyl group (-COH) and at least one amino group (-NH2). Common amines used for gas sweetening are:
Primary amines, Mono Ethanol Amine (MEA) and Di Glycol Amine (DGA)
Secondary amines, Di Ethanol Amine (DEA) and Di Isopropanol Amine (DIPA)
Tertiary amines, Tri Ethanol Amine (TEA) and methyl Di Ethanol Amine (MDEA)
Aspen Hysys Simulation of CO2 Removal From NG with MEA (2)
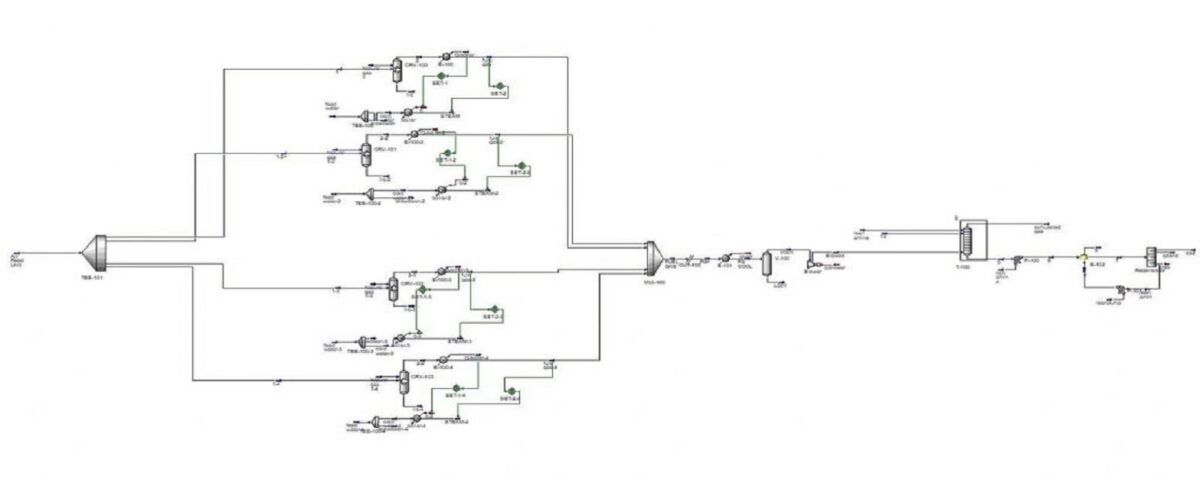
In this project, the natural gas sweetening unit is simulated with MEA in Aspen Hysys software.