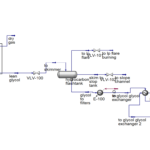
Description
There are different methods to separate the components of a solution. One of these methods is the distillation process. In the distillation method, the components of a mixture are separated based on their boiling point difference. Distillation is done in the following two ways. The first method involves producing vapor by boiling a liquid mixture, then condensing the vapor, without any liquid returning to the distillation chamber. As a result, there is no liquid return. In the second method, a part of the liquefied steam returns to the distiller. And in such a way that this return liquid is placed in the vicinity of the vapor that goes to the refrigerant. Each of these methods can be continuous or batch.
Fractional Distillation Process
Fractional distillation is done in tray or packed distillation column. In this way, the resulting vapors move from the bottom to the top of the column. And it is in contact with the liquid phase that is the condensate of the previous vapors that have been produced along the column and flow downwards. In this way, complete contact is established between the gas and liquid phases. The temperature of each lower tray is lower, and in the distillation column, the temperature decreases from the bottom to the top. Vapors whose condensing point is equal to the temperature of the tray, and on that tray turns into a liquid and collects on it and falls on the lower tray.
As a result of this action, the vapor phase, which is rich in light components, leaves the top of the column, and the liquid phase, which is rich in heavy components, is collected from the bottom. The vapors released from the top of the column are converted into liquid in the condensers and collected as a product. Usually, some of this collected liquid returns to the distillation column as a return liquid to control the temperature of the distillation column. The upper part of the distillation column up to the tray on which the feed is poured is called the “separation column” area, and the lower part of the column related to the feed is called the “stripping” area.
Fractional Distillation of Two-Component and Multi-Component Mixtures
The purpose of distillation is to separate the feed into vapors of almost pure products. In the distillation of two-component systems, the degree of purity is expressed by the mole fraction of the light component in the distillation product XO and in the residue product XB. In two-component systems, from one stage to another, the temperature and equilibrium curve change for the component at the azeotropic point, and one component is more volatile throughout the column. But in multicomponent systems, a component may be more volatile in one part of the column and less volatile in another. which shows the complex nature of component concentration. The phase balance of multi-component systems is much more complicated than that of two-component systems. Because the number of components is large and the balance depends on the temperature and the temperature changes from one stage to another.

Simulation of Distillation of Two Substances With Close BP
Ethylene is obtained through dehydrogenation of ethane. Since the reaction is not complete and the conversion percentage is not complete, there is some ethane in the output that must be separated. The molecular mass and boiling point of ethane and ethylene are very close to each other. Therefore, it is difficult to separate these two substances from each other. In this project, a tray distillation tower is designed and simulated in Aspen Hysys software to separate these two substances.