Description
Gas condensate refers to liquids that exist as gases under reservoir conditions but transform into liquids when temperature and pressure change. These liquids are primarily liquid hydrocarbons found alongside natural gas. Gas condensates hold significant economic value and serve as a crucial energy source and petrochemical feedstock.
Formation of Gas Condensates
Gas condensates form in oil and gas reservoirs due to various factors:
- Temperature and pressure changes: As temperature decreases and pressure increases, lighter gases condense into liquids.
- Changes in Gas Composition: The presence of heavier compounds in natural gas increases the likelihood of condensate formation.
- Geological Processes: Geological processes such as hydrocarbon migration and structural changes in the reservoir also play a role in condensate formation.
Composition of Gas Condensates
The composition of gas condensates varies widely and depends on reservoir conditions and the type of natural gas. Generally, gas condensates primarily consist of paraffinic, naphthenic, and aromatic hydrocarbons. Some of the most important compounds found in gas condensates include:
- Methane: The lightest hydrocarbon and the primary component of natural gas.
- Ethane: A hydrocarbon with two carbon atoms.
- Propane: A hydrocarbon with three carbon atoms.
- Butane: A hydrocarbon with four carbon atoms.
- Pentane and hexane: Heavier hydrocarbons that are major components of gas condensates.
Gas Condensate Separation Processes
Various methods are used to separate gas condensates from natural gas, the most important of which include:
- Distillation: By reducing temperature and increasing pressure, gas condensates are separated from natural gas.
- Adsorption: Adsorbents are used to absorb heavier molecules and separate them from the gas.
- Membrane Separation: Semi-permeable membranes are used to separate different components of the gas mixture.
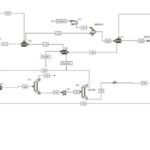
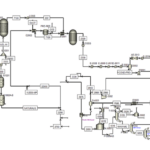
Gas condensate after separation from natural gas contains volatile elements of light hydrocarbons, which can be separated from the liquid phase and cause two-phase system. In order to achieve optimal conditions for storage, transfer and quality improvement, an operation must be carried out to stabilize and adjust the steam pressure. Therefore, the gas condensate stabilization unit is one of the most common and important gas purification process units.
This project is simulated from the following article, which was done exactly with its data:

The simulation was carried out in Aspen Plus version 10 software, which has a detailed work report (10 pages of the report). There is also a simulation file and an Excel file report.
The following is the PDF in the article:
In this project, partial optimization of the unit and economic analysis was also done by Hysys itself, and the report contains explanations about this.