Introduction
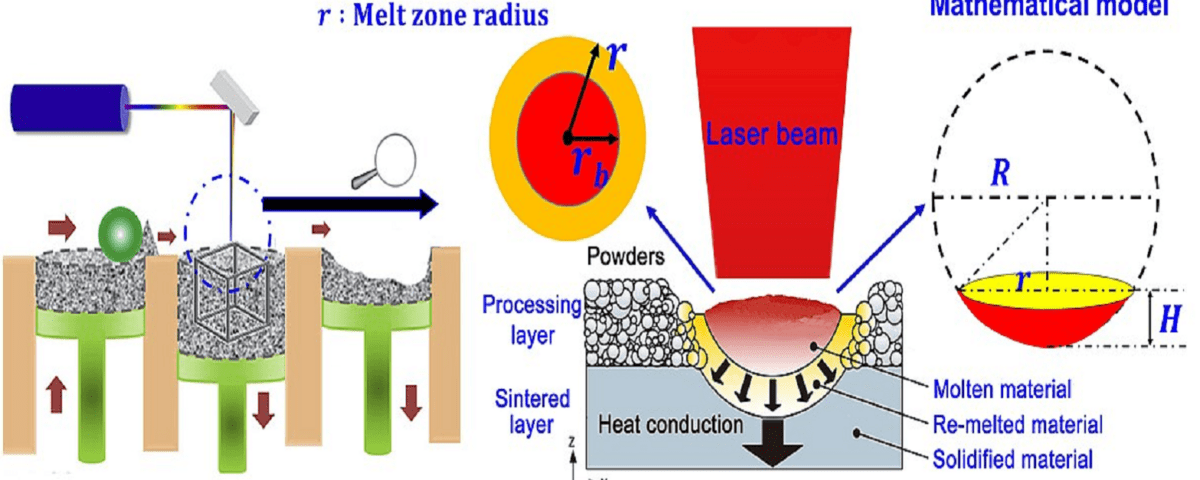
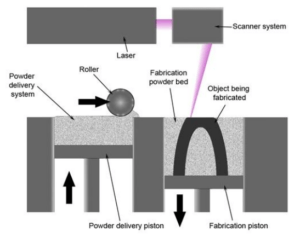
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) is an additive manufacturing process that utilizes a laser to melt metal powder and create three-dimensional structures. Due to its high precision and flexibility, this process is increasingly employed in a wide range of applications, including aerospace, medical, and automotive industries. In SLM, the temperature distribution within the melt pool plays a crucial role in determining the final quality of the component. The temperature distribution influences the grain morphology, thermal stresses, and other material properties. Therefore, accurate determination of the temperature field is essential for precise process control and achieving the desired properties. The heat source path is one of the key factors in determining the temperature field in SLM. The heat source path refers to how the laser moves across the powder surface. Different heat source paths can result in different temperature distributions in the melt pool.
Process Description
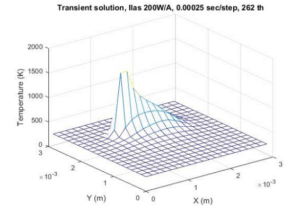
The temperature field of the Selective Laser Melting (SLM) process was investigated for two different patterns to determine which pattern is more effective in reducing the temperature gradient. A three-dimensional transient finite difference model with MATLAB was used to simulate the temperature field of the Inconel 718 powder bed, including phase change. The Hilbert pattern outperformed the chessboard pattern on a suspended platform. This phenomenon results in a reduction of the local temperature gradient and consequently decreases thermal and residual stresses in the solidified metallic part.
Conclusion
The results obtained demonstrate that the Hilbert pattern exhibits a lower temperature gradient compared to the chessboard scan. This is attributed to the relatively slow phase change rate resulting from the arc-shaped sections of the pattern. The SLM process is an additive manufacturing process for producing metal parts with full density, whose properties are comparable to bulk materials. This technology provides an alternative to conventional manufacturing methods such as casting, as it can create complex geometries and features.
Determining The Temperature Field in Selective Laser Melting Process for Different Heat Source Paths
In this project, the temperature field of the Selective Laser Melting process for different heat source paths has been modeled with MATLAB software. The project comes with a complete report (PDF format only).