Introduction
Ammonia, with the chemical formula NH₃, is produced through the Haber process, a reaction between hydrogen and nitrogen under high temperature and pressure. Ammonia has various applications, including the production of fertilizers, nitric acid, explosives, and other nitrogenous compounds. The ammonia unit at LORDEGAN Pet. Co. Complex, with a production capacity of 2050 tons of ammonia per day, is licensed by Casale of Switzerland. The produced ammonia is used as feedstock for urea production within the complex, and any excess is sold.
Process Description of The Ammonia Unit
The gas exiting the secondary reformer undergoes a shift reaction in high- and low-temperature shift reactors to convert carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide. The synthesis gas, now virtually free of carbon dioxide, is directed to the methanation reactor where residual carbon oxides are converted to methane. Due to the low conversion rate of the ammonia synthesis reaction, it is economically advantageous to recycle a portion of the synthesis gas exiting the reactor. This is commonly referred to as the synthesis loop. Therefore, the synthesis gas, after initial compression, is mixed with the gas exiting the synthesis reactor and, after final compression, enters the catalytic synthesis reactor. The produced ammonia is sent to the urea unit for consumption, and the excess, after cooling, is sent to the cold storage tank.
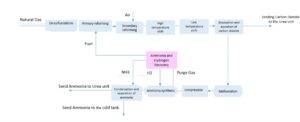
The Ammonia Production Process From Natural Gas Generally Involves The Following Main Steps:
- Desulfurization of Natural Gas: This step involves removing sulfur compounds from the natural gas to protect catalysts used in subsequent processes.
- Reforming: In this step, natural gas is reacted with steam over a nickel catalyst to produce a synthesis gas mixture, primarily consisting of hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
- Methanation: The synthesis gas is passed over a catalyst to convert any remaining carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide to methane, which is more inert and does not interfere with the ammonia synthesis process.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal: Carbon dioxide is removed from the synthesis gas to increase the hydrogen-to-nitrogen ratio, which is optimal for ammonia synthesis.
- Ammonia Synthesis: The purified synthesis gas, consisting primarily of hydrogen and nitrogen, is reacted over an iron catalyst under high temperature and pressure to produce ammonia.
Ammonia Recovery Unit
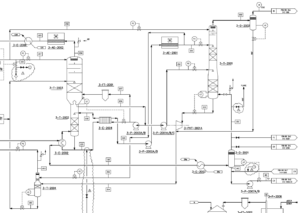
In the ammonia recovery unit at LORDEGAN Pet. Co. Complex (see figure below), ammonia is recovered from waste gases, or purge gas, through a sequential absorption (Tower 3001-T) and desorption (Tower 3002-T) process using water. The ammonia-rich water is produced at the top of Tower 3002-T.
Two Primary Issues Have Been Identified With This Unit:
-
High Operating Pressure in Tower 3002-T:
The high operating pressure of 1990 kPa, in addition to reducing mass transfer efficiency, leads to increased steam consumption in the reboiler to generate vapor for mass transfer with the liquid in the tower packings.
-
Significant Consumption of High-Pressure Steam:
Particularly in the reboiler of Tower 3002-T, the high-pressure steam consumption is notable.
At the reboiler pressure of 1990 kPa, the bottom product (solvent without ammonia) has a temperature of 211°C, resulting in a high utility consumption of 432,480 kg/day for cooling (cooling water).
Currently, in the 300 ammonia unit at the petrochemical complex, ammonia is absorbed from a gas mixture (hydrogen, nitrogen, and methane) using water.
Conclusion
The results showed that:
a) 100% recovery of cooling water was done using process integration.
b) No need for high pressure steam and recovery of all steam used in the current process.
c) Removing the reboiler from the system and using low pressure steam directly and determining its optimal flow rate equal to 1500 kg/h.Using the technical knowledge and advanced simulation tools, the expert team of SANILCO succeeded in creating a fully compatible simulation model of the Kermanshah Petrochemical Reforming Unit with an accuracy of less than 10%. This model is a powerful tool for in-depth analysis of the unit’s performance and improving its productivity. is coming.
In order to improve the performance and productivity of LORDEGAN Pet. Co. Ammonia Production Unit, SANILCO Company conducted comprehensive simulation and optimization studies on the key equipment and processes of this unit. These studies include the following:
Simulation and optimization of tower T-3802 (ammonia separation) of LORDEGAN Pet. Co.
Simulation of LORDEGAN Pet. Co. ammonia separation and recovery unit under Casale license
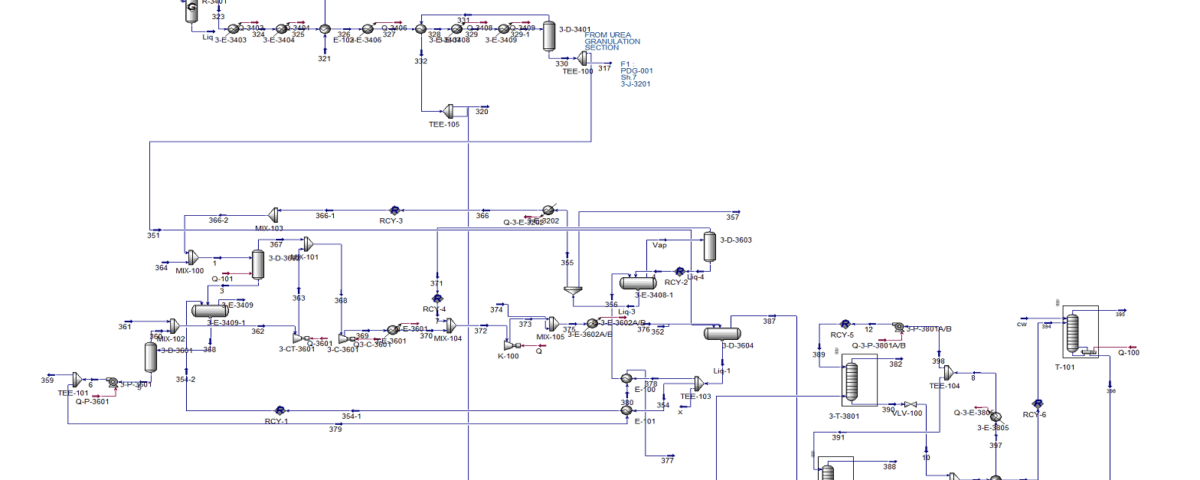
Optimizing and reducing the costs of the distillation tower for the separation of ammonia and water (LORDEGAN Pet. Co.)Simulation of LORDEGAN Pet. Co. Ammonia Separation and Recovery Unit Under Casale License
In this project, the simulation process of LORDEGAN Pet. Co. Ammonia Separation and Recovery Unit under Casale license has been simulated with Aspen Hysys version 14 software.
-