Introduction
Liquefied natural gas or LNG is natural gas that is temporarily converted into a liquid state for storage or transportation in large volumes. Now, it mostly consists of methane (more than 90 percent) and may contain some ethane, propane, butane, and some other heavy alkanes. The LNG refining process can be designed in such a way that the final product contains 100% methane. LNG has a volume equal to 1/600 of the volume of natural gas in gaseous state. Liquid gas is odorless, colorless, non-toxic and non-corrosive, The dangers that this gas can cause include flaming, freezing and suffocation. The energy density of LNG is 60% of diesel fuel.
The intermediate process involves the removal of compounds such as dust, acid gases, helium, water and heavy hydrocarbons that cause problems for the gas in the downstream flow (transportation of gas in pipes). After removing the above, the natural gas is cooled at a pressure equal to the pressure and temperature of -162 degrees Celsius. (Maximum gas pressure for transmission applications is 25 kPa or 3.6 psi).
LNG Production
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is essentially natural gas that has been cooled to a very low temperature until it becomes a liquid. Imagine placing gas in a very powerful freezer until it becomes extremely cold. When the gas becomes very cold, it turns into a liquid. This causes the volume of the gas to decrease significantly, making it easier to transport.
LNG Storage
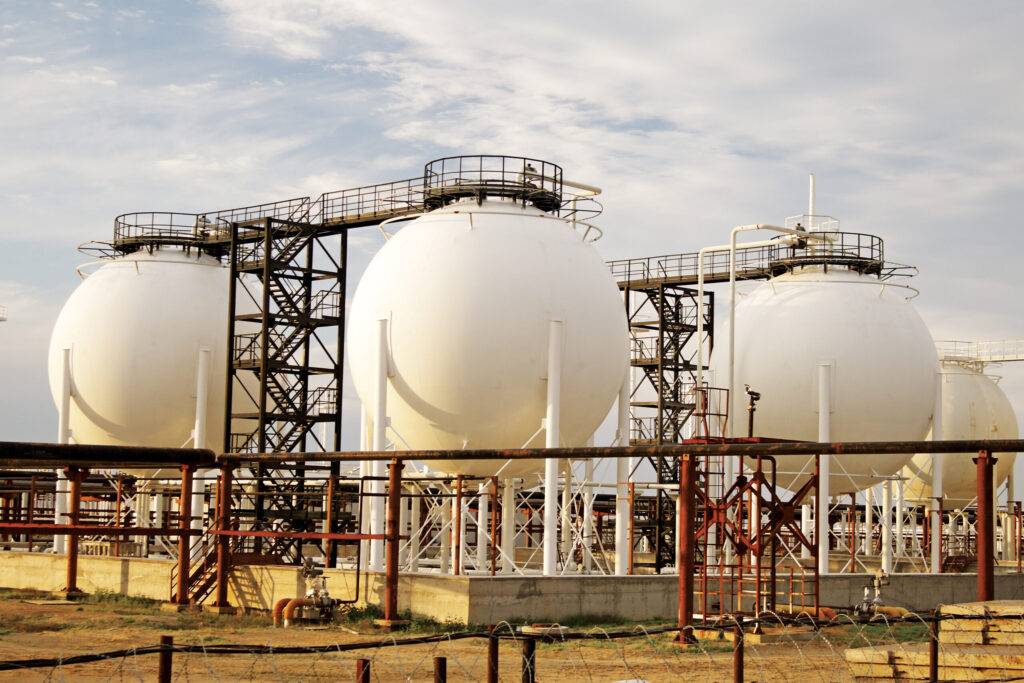
Due to its significantly smaller volume compared to its gaseous state, liquefied natural gas (LNG) requires specific conditions for storage. These conditions are designed to maintain the extremely low temperature of LNG and prevent its vaporization.
Characteristics of LNG storage tanks:
- Very Strong Insulation: These tanks must be insulated in such a way that they can maintain the very low temperature of LNG. Insulation materials typically include polyurethane foams or vacuum panels.
- Resistant Material: The tank body must be made of a material resistant to very low temperatures and pressure. Special steels are usually used to construct these tanks.
- Special Design: The shape of LNG tanks is usually spherical or cylindrical to minimize the surface area in contact with the external environment and prevent heat loss.
Types of LNG Storage Tanks:
- Land-based Tanks: These tanks are installed permanently at the site of LNG consumption or production.
- Marine Tanks: These tanks are installed on LNG ships and used for transporting LNG.
Economic Analysis Report
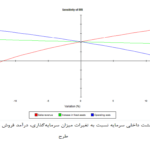
The production of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is a complex and capital-intensive process that requires a thorough economic analysis. This analysis considers numerous factors such as capital investment costs, operating expenses, LNG selling price, Internal Rate of Return (IRR), payback period, and project sensitivity to changes in key variables.
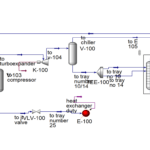
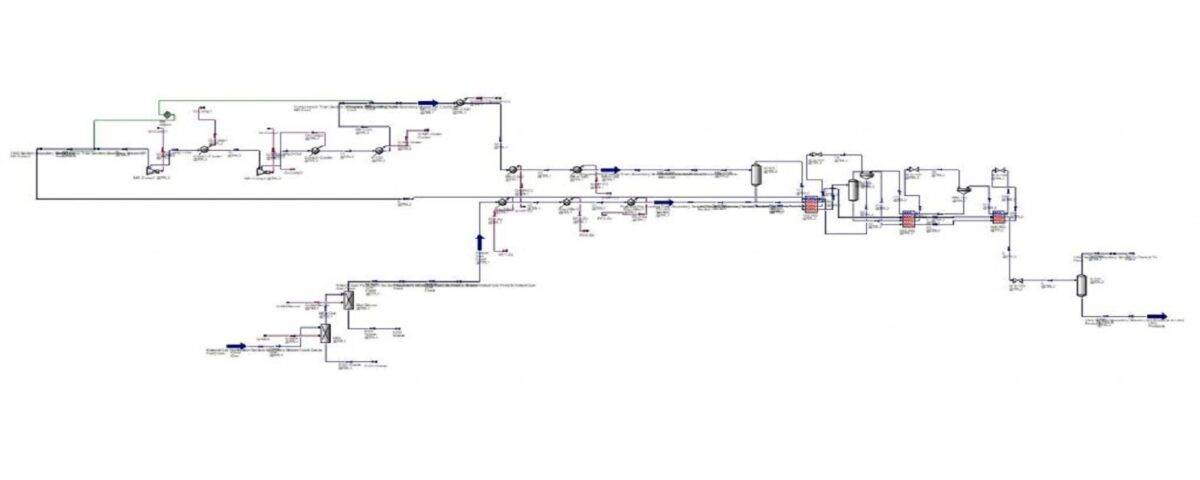
This project was initially simulated using the HYSYS software, and subsequently, an economic analysis was conducted within the same software. Comprehensive Word documents containing textual reports are available, along with visual tutorials covering the entire unit. This simulation project was undertaken for a thesis, and only chapters 3 and 4, which comprise the software report, were delivered to the project owner.
Conclusion
An economic analysis of LNG production is an indispensable tool for making investment decisions in this industry. Given the complexities and risks involved, conducting a comprehensive and thorough economic study prior to initiating any project is essential.