Application of Work Breakdown Structure
The WBS is so widely applicable in project environments that it can be considered the heart of project management.
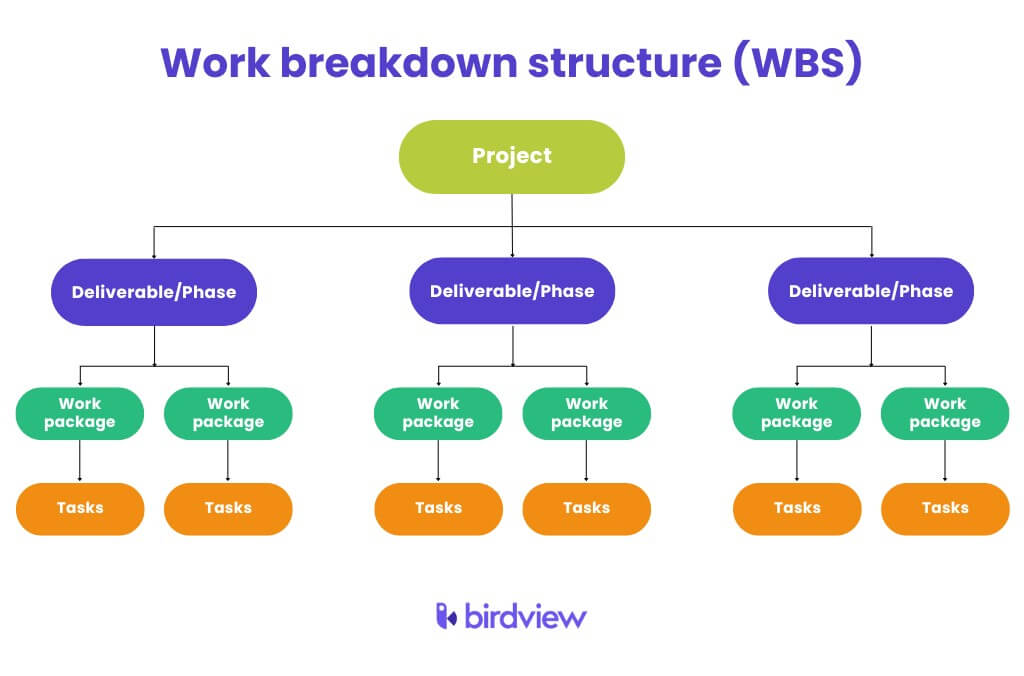
In a project, the WBS provides a hierarchical breakdown of deliverables, which are tangible and measurable outcomes essential for completing the project and must be approved by the client.
Types of Work Breakdown Structures
It is important to note that the basis for the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) varies across different projects, and numerous WBS formats can be developed based on project objectives. Here, we introduce the most well-known types of WBS:
Phase or Stage Breakdown Structure: This structure organizes the project based on the phases or stages of work.
Department Breakdown Structure: This WBS categorizes the project according to the various organizational departments involved.
Assembly/Product Breakdown Structure: This structure breaks down the project based on the assembly of the final product.
Contractor Breakdown Structure: This WBS organizes the project based on the contractors involved.
System Breakdown Structure: This structure categorizes the project based on the systems required for its completion.
Transport Breakdown Structure: This WBS organizes the project according to transportable items.
Cost Breakdown Structure: This structure breaks down the project by costs associated with different elements.
Software for Creating Work Breakdown Structures
If you need to create a WBS, you can use the following software:
Visio: A Microsoft Office application that can be easily used to draw WBS diagrams.
WBS CHART PRO: This software is used to create graphical representations of the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) for a summary view of hierarchical information.
MSP (Microsoft Project): This specialized project control software allows you to create a WBS effectively.
Conclusion
Managing complex projects, especially in industries such as oil, gas, petrochemicals, and construction, requires the use of advanced tools and methods. The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) serves as an organized framework that divides the project into smaller, manageable components, providing the necessary clarity for planning and execution. The Gantt Chart, with its visual representation of scheduling and progress, helps managers effectively allocate resources and steer the project in the right direction. Furthermore, EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) projects combine these tools to offer a comprehensive framework for managing large and multi-phase projects.
SANILCO, leveraging its specialized and experienced team, possesses expertise in advanced project management tools such as WBS and Gantt Charts, enabling it to plan, execute, and control complex EPC projects. With a strong foundation in cutting-edge technical knowledge and practical experience in refining, petrochemicals, and energy sectors, the company is capable of providing efficient and cost-effective solutions for project management. Anil Pars’s ability to utilize tools like WBS and Gantt Charts, along with precise process simulations, has made it a reliable partner for executing large and challenging projects.
Given these capabilities,
SANILCO can not only successfully manage EPC projects but also create significant added value for its clients by optimizing time, cost, and quality. By relying on innovation and advanced technologies, the company has taken important steps toward advancing the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries, playing a key role in achieving global standards.