Introduction
In the chemical and process industries, the design and optimization of processes hold significant importance. One of the key tools in this regard is the creation of Process Flow Diagrams (PFD), which provide a comprehensive overview of the process, illustrating the main components, as well as the flow of materials and energy. These diagrams not only aid in a better understanding of the process but also serve as a foundation for conducting precise simulations and engineering analyses. Process simulations can be performed using specialized software such as Aspen Plus. This software offers powerful tools that facilitate the modeling and simulation of chemical processes, allowing engineers to examine the behavior of complex systems under various conditions.
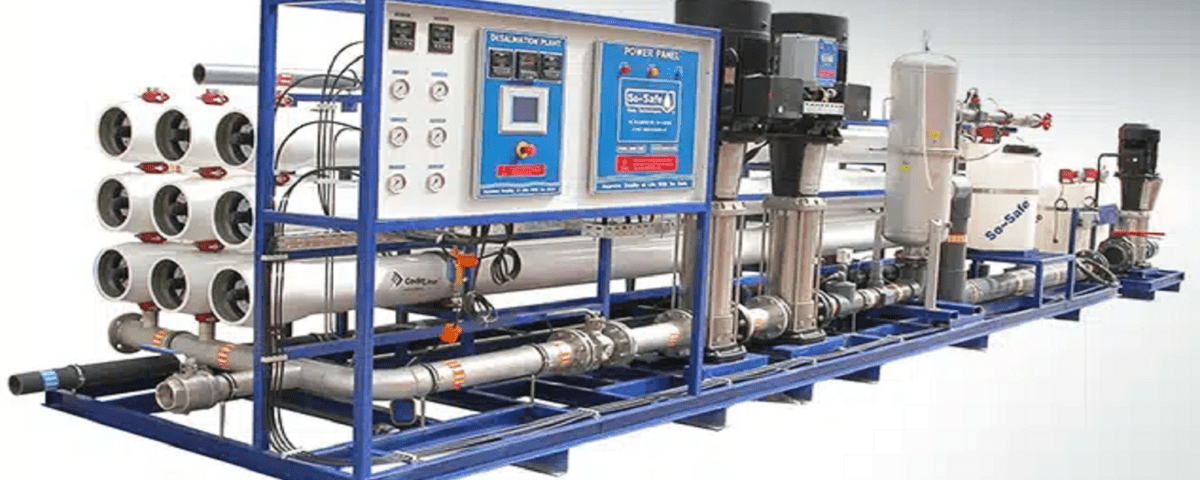
This study focuses on the simulation of the distilled water production process. Due to its high purity and the absence of mineral and organic impurities, distilled water has extensive applications in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food, laboratories, and even in cooling systems and batteries. The production process of distilled water typically involves stages such as evaporation, distillation, and condensation, where raw water is converted into vapor by heating and subsequently collected as distilled water upon cooling.

The system includes various stages such as Cartridge Filtration, Activated Carbon Filtration, Reverse Osmosis (RO), and Flash Evaporation. Below is a detailed explanation of each of these stages:
1. Cartridge Filtration
Objective: To remove suspended solid particles from water, such as sand, silt, and other physical contaminants.
Operation: Raw water initially passes through the cartridge filter. These filters are usually made of polypropylene and have very fine pores (typically ranging from 1 to 20 microns).
Outcome: After passing through this filter, the water is free from suspended solid particles and is ready to enter the next stage.
2. Activated Carbon Filtration
Objective: To remove chlorine, organic compounds, and unpleasant odors and tastes from the water.
Operation: After passing through the cartridge filter, the water enters the activated carbon filter. Activated carbon, due to its high surface area, is capable of adsorbing chlorine and organic compounds.
Outcome: After this stage, the water is free from chlorine and organic compounds, making it ready for the Reverse Osmosis stage.
3. Reverse Osmosis (RO)
Objective: To remove dissolved minerals, ions, and other impurities from the water.
Operation: Water is forced through a semi-permeable membrane under high pressure. This membrane allows only water molecules to pass through while removing ions and dissolved minerals.
Outcome: The output water from this stage is deionized water with high purity. However, there may still be some very fine impurities present.
4. Flash Evaporation
Objective: To remove remaining impurities and produce distilled water with very high purity.
Operation: The deionized water from the RO stage enters a flash evaporation chamber. In this chamber, the pressure is suddenly reduced, causing the water to evaporate rapidly. The produced water vapor is then condensed and collected as distilled water.
Outcome: The output water from this stage is distilled water with very high purity, suitable for sensitive applications such as laboratories, pharmaceutical industries, and electronics.

5. Electrical Panel
Objective: To control and monitor all electrical equipment and instrumentation in the system.
Main Components:
PLC Controllers: For process automation and equipment control.
Inverters: For controlling pump speed and optimizing energy consumption.
Electrical Protections: Such as circuit breakers and protective relays.
Monitoring: Displaying process parameters such as pressure, temperature, flow rate, and water quality.

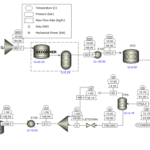
Process Flow Diagram (PFD)
Input: Raw Water
Stages:
Cartridge Filter، Activated Carbon Filter، Reverse Osmosis (RO)، Flash Evaporation
Output: Distilled Water
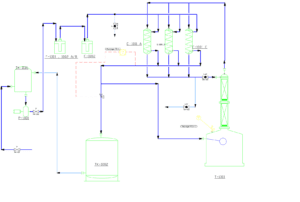
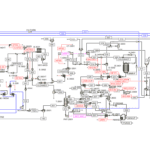
Simulation in ASPEN PLUS
Cartridge and Activated Carbon Filtration: These stages are typically simulated simply using separator blocks in ASPEN PLUS.
Reverse Osmosis: Specialized reverse osmosis blocks are utilized in ASPEN PLUS, taking into account parameters such as pressure, flow rate, and salt concentration.
Flash Evaporation: This stage is simulated using flash drum and distillation column blocks in ASPEN PLUS.

SANILCO
SANILCO is recognized as a pioneer in the industry, possessing extensive capabilities in simulation, optimization, design, and construction of various processes. With a skilled engineering team and advanced technologies, the company is capable of effectively executing complex industrial projects.
In the field of engineering procurement projects, the company has successfully designed, constructed, and commissioned a semi-industrial distilled water unit with a capacity of 120 tons per year. Leveraging its past experiences and technical knowledge, Anil Pars Process Industry Company is not only adept in similar projects but also in the development and improvement of other production processes. The company provides its clients with optimal and cost-effective solutions, always designed in accordance with international standards and their specific needs.
Sample Completed Projects
Pre-Feasibility Project of Sea Water Desalination Unit With RO
Conclusion
The engineering, procurement, and commissioning project of the semi-industrial distilled water unit with a capacity of 120 tons per year is particularly significant in the area of process design and simulation using Aspen Plus software, as well as in the preparation of Process Flow Diagrams (PFD). In this project, SANILCO has utilized its technical and engineering expertise to achieve an optimized and efficient design for this unit.
The results of this project include the design of effective systems for producing high-quality distilled water, reducing operational costs, and optimizing energy consumption. Through simulation and data analysis in Aspen Plus, the company has managed to design processes that achieve the highest efficiency with minimal waste.